As the world becomes increasingly connected, the demand for high-speed internet continues to grow. Enter Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) networks, the future of connectivity. HFC networks offer a practical and cost-effective solution to meet the surging demand for fast and reliable internet access. By integrating existing coaxial infrastructure with fiber optic technology, HFC networks combine the advantages of both, providing efficient and scalable connectivity.
HFC systems consist of fiber cables that extend from the service provider’s central office to neighborhood nodes, where coaxial cables distribute services to individual users. This integration ensures high bandwidth capacity, low latency, and long-distance transmission capabilities, making HFC networks the preferred choice for modern communication systems. With HFC networks, users can enjoy seamless internet access for a wide range of activities, from streaming videos to online gaming, all with exceptional speed and reliability.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into how HFC networks are structured and how they navigate data flow, exploring the advantages this hybrid connectivity offers. We’ll also discuss the surging demand for high-speed broadband and how HFC networks are playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing connectivity in the digital age. Join us on this journey into the future of connectivity with HFC networks.
How HFC Networks are Structured
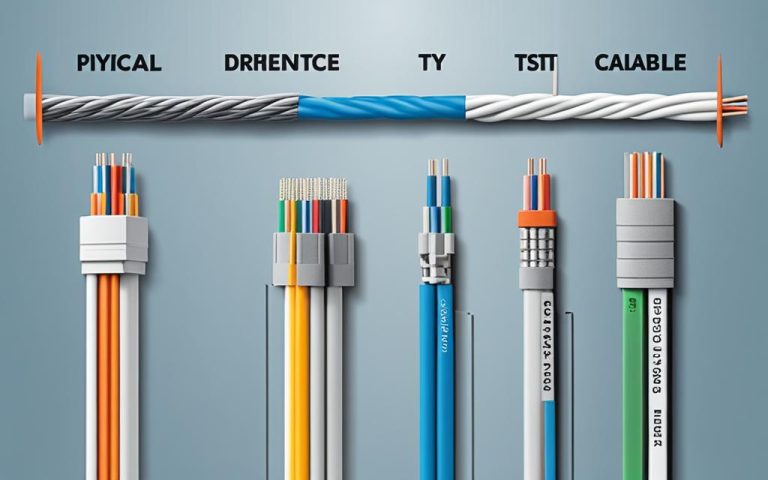
HFC networks, short for Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial networks, are ingeniously structured by integrating both fiber optic cables and coaxial cables. This strategic integration allows for efficient and cost-effective connectivity. Let’s take a closer look at the structure of HFC networks:
- Fiber Optic Cables: The backbone of HFC networks is formed by fiber optic cables that extend from the central office to neighborhood nodes. These fiber cables enable high bandwidth communication, low latency, and long-distance transmission capabilities. With their ability to carry large amounts of data at incredible speeds, fiber optic cables lay the foundation for seamless connectivity.
- Neighborhood Nodes: At the neighborhood nodes, the fiber optic signals are converted into electrical signals. This conversion allows for seamless integration with existing coaxial infrastructure.
- Coaxial Cables: From the neighborhood nodes, coaxial cables take over the distribution of services to individual users. These coaxial cables are responsible for delivering services like cable TV and broadband access to households.
This hybrid approach optimizes the existing coaxial infrastructure while incorporating the advanced capabilities of fiber optics. By leveraging the strengths of both technologies, HFC networks offer high-speed connectivity that is affordable and accessible to a wide range of users.
Let’s visualize the structure of HFC networks:
| Fiber Optic Cables | Neighborhood Nodes | Coaxial Cables |
|---|---|---|
| High bandwidth Low latency Long-distance transmission | Fiber to electrical signal conversion | Service distribution to users |
By combining the benefits of fiber optics and coaxial cables, HFC networks provide a robust infrastructure for modern communication needs. This structure ensures efficient transmission of data, allowing users to enjoy high-speed internet access and a multitude of services.
Navigating Data Flow in HFC Applications
Data flows in HFC applications in two directions: downstream and upstream. Understanding the data transmission process is key to optimizing the performance and reliability of HFC networks.
Downstream Data Flow:
Downstream data refers to information that travels from the central office to the optical node, where the fiber cable signals are converted into electrical signals. This conversion allows the data to be transmitted effectively over the coaxial cables.
The downstream data flow can be visualized as follows:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data is transmitted from the central office through fiber optic cables. |
| 2 | At the optical node, fiber cable signals are converted into electrical signals. |
| 3 | The electrical signals are divided into multiple signals to be distributed over coaxial cables. |
| 4 | The distributed signals reach users’ cable modems, allowing them to access internet services. |
Upstream Data Flow:
Upstream data refers to user requests, feedback, and other information that travels from the cable modems to the central office. This data flow enables users to send data back to the service provider and interact with online platforms.
The upstream data flow can be summarized as follows:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Users’ requests and feedback are initiated on their cable modems. |
| 2 | The cable modems convert the requests and feedback into electrical signals. |
| 3 | The electrical signals are transmitted through the coaxial cables. |
| 4 | The data reaches the central office, allowing service providers to process and respond to user interactions. |
HFC networks ensure efficient and reliable data transmission in both downstream and upstream directions, enabling users to access high-speed internet services and communicate effectively in the digital era.
Advantages of Hybrid Connectivity
HFC networks offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for modern communication systems. These advantages include:
- High-speed internet access with significant bandwidth capacity: HFC networks combine the speed of fiber optics with the extensive coverage of coaxial cables, providing users with fast and reliable internet connectivity. This ensures smooth browsing, seamless streaming, and quick downloads, meeting the increasing demands of data-intensive applications.
- Scalability to accommodate increasing bandwidth and newer technologies: HFC networks are designed to be easily upgradeable, allowing service providers to enhance bandwidth capacity and incorporate new technologies without the need for extensive infrastructure changes. This scalability ensures that HFC networks can keep up with evolving communication needs and advancements in technology.
- Controlled costs by utilizing existing coaxial infrastructure: One of the key advantages of HFC networks is their ability to leverage the existing coaxial infrastructure. Rather than completely replacing the infrastructure, HFC networks make strategic use of the existing cables, significantly reducing the cost of deployment and ensuring cost-effective communication solutions.
- Broad availability of multiple services: HFC networks enable the delivery of multiple services over a single network, including television, video streaming, and voice over IP (VoIP) telephony. This broad availability of services provides users with a convenient and comprehensive communication experience, all through a single connection.
- Network reliability through optimized use of existing coaxial infrastructure and selective deployment of fiber optics: HFC networks utilize a hybrid approach, combining the reliability of coaxial cables with the high-speed capabilities of fiber optics. By strategically deploying fiber optics where needed and optimizing the use of existing coaxial infrastructure, HFC networks ensure a reliable and robust network that can withstand environmental factors and deliver consistent performance.
Overall, the advantages of HFC networks make them a preferred choice for efficient and scalable connectivity, offering high-speed internet access, controlled costs, broad service availability, and network reliability.
Take a look at the following table for a visual representation of the advantages of HFC networks:
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| High-speed internet access with significant bandwidth capacity | Combines fiber optics and coaxial cables to provide fast and reliable internet connectivity |
| Scalability | Can accommodate increasing bandwidth and integrate newer technologies without major infrastructure changes |
| Controlled costs | Utilizes existing coaxial infrastructure, reducing deployment costs |
| Broad availability of multiple services | Enables the delivery of TV, video streaming, and VoIP telephony over a single network |
| Network reliability | Optimized use of existing coaxial infrastructure and selective deployment of fiber optics ensure a robust and dependable network |

The Surging Demand for High-Speed Broadband
The global HFC market has experienced significant growth, driven by the surging demand for high-speed internet and advanced communication services. As the digital age continues to evolve, the need for fast and reliable connectivity has become essential in both personal and professional spheres. This increasing demand has paved the way for the exponential growth of the HFC market.
According to market research, the HFC market is projected to reach a value of $12.2 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7%. This growth can be attributed to the rising popularity of bandwidth-intensive applications such as streaming services and online gaming, which require robust and high-speed broadband connections.
The HFC technology, with its unique ability to deliver high-speed and reliable connectivity, is poised to meet the growing demands of today’s digital world. By integrating existing coaxial infrastructure with fiber optic technology, HFC networks offer an efficient and cost-effective solution to ensure seamless data transmission and satisfy the surging demand for high-speed broadband.
Key Drivers of HFC Market Growth:
- Increase in bandwidth-intensive applications
- Growing need for reliable and high-speed internet
- Rapid digital transformation in various sectors
- Expanding adoption of smart devices and IoT
- Enhanced user experience in content consumption and online activities
“Surging demand for high-speed broadband is reshaping the HFC market, driving innovation and technological advancements. As more consumers and businesses rely on fast and reliable internet access, the importance of HFC networks in meeting these demands cannot be overstated.”
In response to the surging demand, industry players are continuously exploring ways to enhance the capabilities of HFC networks, ensuring they remain at the forefront of the connectivity landscape. This includes advancements in optical transmission technologies, improved network management systems, and the development of new communication protocols tailored to meet the specific needs of high-speed data transfer.
As the HFC market continues to grow, it is crucial for service providers to proactively invest in network infrastructure to ensure they can fulfill the rising demand for high-speed broadband. This will enable them to stay competitive in the rapidly evolving digital landscape and cater to the diverse needs of consumers and businesses alike.
| Market Value | CAGR |
|---|---|
| $12.2 billion | 7% |

Conclusion
Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) networks are paving the way for the future of connectivity. This innovative solution seamlessly integrates fiber optic and coaxial infrastructure, providing a practical and cost-effective approach to meet the surging demand for high-speed internet. With HFC networks, users can enjoy efficient and scalable connectivity, making it possible to stream high-definition content, engage in online gaming, and utilize bandwidth-intensive applications with ease.
One of the key advantages of HFC networks is their structured design, which ensures seamless data flow in both downstream and upstream directions. This means that users can experience fast and reliable internet access, while also being able to send their requests and feedback to service providers with ease. Such bidirectional data transmission capabilities make HFC networks a reliable choice for businesses and individuals alike.
Beyond speed and efficiency, HFC networks offer multiple advantages that further solidify their position as the future of connectivity. From high-speed internet access and scalability to controlled costs and broad service availability, HFC networks empower users to stay connected and productive. Additionally, the integration of existing coaxial infrastructure with fiber optics brings about network reliability, allowing for stable connections and enhanced user experiences.
As the demand for high-speed broadband continues to surge, HFC networks are well-positioned to meet and exceed expectations. With their ability to deliver fast and reliable connectivity, HFC networks are revolutionizing the way we connect in the digital world. Whether it’s for personal or professional use, HFC networks offer a robust and future-proof solution that enables us to stay connected and thrive in the era of digital communication.
FAQ
What are HFC networks?
HFC networks, also known as Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial networks, are a practical and cost-effective solution to meet the growing demand for high-speed internet. These networks integrate existing coaxial infrastructure with fiber optic technology, combining the advantages of both to provide efficient and scalable connectivity.
How are HFC networks structured?
HFC networks are structured by integrating fiber optic cables and coaxial cables. The fiber cables extend from the service provider’s central office to neighborhood nodes, providing high bandwidth, low latency, and long-distance transmission capabilities. From the optical node, the coaxial cables distribute services like cable TV and broadband access to users. This hybrid approach optimizes existing infrastructure while incorporating new fiber technology, making high-speed connectivity affordable and accessible.
How does data flow in HFC applications?
Data flows in HFC applications in two directions: downstream and upstream. Downstream data, including internet services, travels from the central office to the optical node, where fiber cable signals are converted into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then divided into multiple signals and distributed over coaxial cables to users’ cable modems. Upstream data, such as user requests and feedback, travels in the opposite direction, from users’ cable modems to the central office. HFC networks ensure efficient and reliable data transmission in both directions.
What are the advantages of HFC networks?
HFC networks offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for modern communication systems. These advantages include high-speed internet access with significant bandwidth capacity, scalability to accommodate increasing bandwidth and newer technologies without major infrastructure changes, controlled costs by utilizing existing coaxial infrastructure, broad availability of multiple services like TV, video streaming, and voice over IP (VoIP), and network reliability through the optimized use of existing coax cable infrastructure and selective deployment of fiber optics.
What is driving the demand for high-speed broadband?
The global HFC market has witnessed significant growth due to the surging demand for high-speed internet and advanced communication services. The market is projected to reach a value of .2 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate of 7%. The increasing demand for bandwidth-intensive applications like streaming services and online gaming is a key driver of market expansion. HFC technology, with its ability to deliver high-speed and reliable connectivity, is poised to meet the growing demands of the digital age.
What is the future of connectivity?
Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) networks represent the future of connectivity, providing a practical and cost-effective solution to meet the surging demand for high-speed internet. These networks integrate fiber optic and coaxial infrastructure, offering efficient and scalable connectivity. HFC networks are structured to ensure seamless data flow in both downstream and upstream directions. They offer advantages such as high-speed internet access, scalability, controlled costs, broad service availability, and network reliability. With the surging demand for high-speed broadband, HFC networks are playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing connectivity in the digital world.