Personal health devices have undergone significant advancements in recent years with the integration of technologies such as wireless body area networks (WBANs) and smartphones. This integration enables seamless monitoring of vital signs and physical activity, providing real-time health information to individuals, healthcare providers, and researchers.
Personal Area Networks (PANs) now encompass the monitoring of vital signs using wearable sensors placed on or in the body. These sensors communicate with smartphones, transmitting data to centralized systems for proactive health management and potential early intervention based on personalized data.
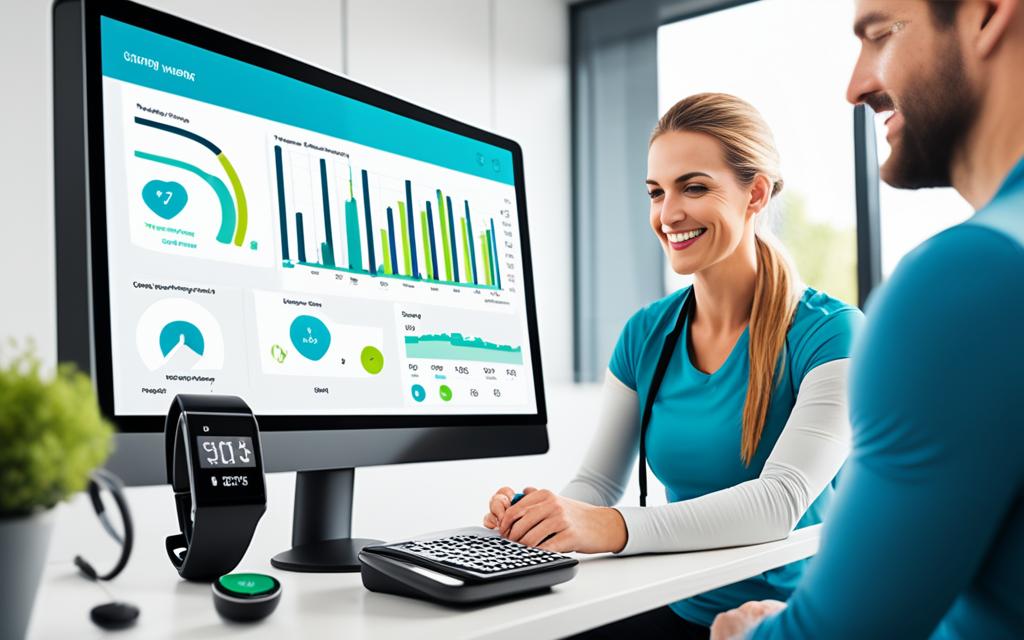
With the growing popularity of wearable sensors and smartphones, personal health monitoring has become more accessible and convenient. Wearable sensors collect data on vital signs, physical activity, and other health-related metrics, while smartphones act as the central hub for data collection, processing, and communication in personal health monitoring systems.
Integration with PANs allows for remote monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to access real-time data and make informed decisions about patient care. This interconnectedness empowers individuals to take control of their health and facilitates preventive and proactive healthcare practices.
In the following sections, we will explore the benefits of mHealth, the role of wearable sensors and smartphones in personal health monitoring, the future of personal health devices and PAN integration, and conclude with the potential advancements in this exciting field.
The Benefits of mHealth and Wireless Personal Health Monitoring
mHealth, or mobile health, is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by leveraging advancements in informatics, smartphones, and miniaturized sensors. Wireless personal health monitoring systems, such as WBANs, offer numerous benefits. They allow for continuous monitoring of vital signs and physical activity, providing users with real-time health information. This data can be transmitted directly to healthcare providers and researchers, leading to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. By aggregating this data into centralized databases, it becomes a valuable resource for population health management and research.
With mHealth, individuals can take control of their health by accessing real-time health information through smartphone integration and wearable sensors. This enables proactive health management and the potential for early intervention based on personalized data. The integration of sensor systems and smartphones in personal health monitoring empowers individuals to monitor their health from anywhere, at any time, leading to improved healthcare outcomes.
The Advantages of mHealth and Wireless Personal Health Monitoring:
- Continuous monitoring of vital signs and physical activity
- Real-time access to personal health information
- Enhanced accuracy in diagnoses and personalized treatment plans
- Remote data transmission to healthcare providers and researchers
- Centralized databases for population health management and research
By leveraging sensor systems, smartphones, and aggregated databases, mHealth is transforming the way individuals monitor and manage their health. This technology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by improving access to timely and accurate health information. With the integration of mHealth and wireless personal health monitoring, individuals can take a proactive approach to their well-being and healthcare providers can make better-informed decisions for more targeted and effective treatments.
The Role of Aggregated Databases in Personal Health Monitoring
Aggregated databases play a crucial role in mHealth and wireless personal health monitoring. These databases store and analyze data collected from various sources, such as wearable sensors and smartphone apps. By consolidating data from multiple users, aggregated databases provide valuable insights into population health trends and contribute to medical research.
Wearable Sensors and the Role of Smartphones in Personal Health Monitoring
Wearable sensors are essential components in personal health monitoring systems as they collect crucial data related to vital signs, physical activity, and other health metrics. These sensors are seamlessly integrated into various wearable devices, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, enabling individuals to conveniently track their health on the go.
Smartphones play a pivotal role in these monitoring systems by serving as the central hub for data collection, processing, and communication. They wirelessly connect to the wearable sensors, collect the data, and transmit it to the cloud or a centralized system. This enables remote monitoring, empowering healthcare providers to access real-time data and make informed decisions about patient care, even from a distance.
By leveraging the power of wearable sensors and smartphones, personal health monitoring has become more accessible and efficient. Users can track their health in real-time, monitor trends over time, and proactively manage their well-being. Healthcare providers can benefit from the continuous and comprehensive data collection, enabling accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and preventive interventions.
To illustrate the importance of wearable sensors and smartphones in personal health monitoring, consider the following scenario:
A patient with a chronic health condition wears a smartwatch with integrated wearable sensors to monitor their heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity. The smartwatch wirelessly transmits this data to the patient’s smartphone, which securely stores and analyzes the information. The smartphone then shares the data with the patient’s healthcare provider, who can remotely monitor the patient’s health, identify any concerning trends or abnormalities, and intervene if necessary.
This seamless integration of wearable sensors with smartphones revolutionizes personal health monitoring by providing individuals with timely and actionable insights into their well-being. It enhances the ability of healthcare providers to deliver personalized care, especially in remote or inaccessible areas. The combination of wearable sensors and smartphones opens up new possibilities for remote monitoring, telemedicine, and preventive healthcare.
Overall, wearable sensors and smartphones are key components in personal health monitoring, enabling data collection, health tracking, and remote monitoring. They empower individuals to take control of their health while providing healthcare providers with valuable insights for better patient care.
Example of wearable sensors integrated with smartphones in personal health monitoring:
| Wearable Device | Supported Sensors | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Apple Watch Series 6 | Optical heart rate sensor, Electrical heart sensor, ECG sensor | Continuous heart rate monitoring, Blood oxygen level tracking, ECG recordings |
| Fitbit Charge 4 | Optical heart rate sensor, GPS, Accelerometer | Heart rate monitoring, Sleep tracking, Activity tracking with built-in GPS |
| Samsung Galaxy Watch Active2 | Optical heart rate sensor, Electrical heart sensor, ECG sensor, Accelerometer, Gyroscope | Heart rate monitoring, ECG recordings, Fall detection, Sleep tracking |

The Future of Personal Health Devices and PAN Integration
The future of personal health devices and the integration of Personal Area Networks (PANs) hold great promise in the field of healthcare. With advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics, personalized healthcare is on the horizon. By analyzing patient data, AI can provide tailored treatment plans and interventions.
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) will play a crucial role in connecting personal health devices to larger healthcare systems. This connectivity will enable seamless data exchange and collaboration between patients, healthcare providers, and researchers, revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered.
Predictive Analytics in Personalized Healthcare
The integration of predictive analytics into personal health devices will transform the way individuals manage their health. By leveraging AI algorithms and machine learning, these devices will be able to predict health outcomes and identify potential risks before they escalate. This proactive approach to healthcare will lead to early interventions, reducing the burden on healthcare systems and improving patient outcomes.
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) in Healthcare
The IoMT will connect personal health devices to a network of interconnected medical devices, allowing for comprehensive and real-time health monitoring. This interconnected ecosystem will enable healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients, access vital health data, and provide timely interventions. Additionally, researchers will have access to a wealth of data for population health management and groundbreaking medical research.
With the integration of PANs and the IoMT, the possibilities for personalized and proactive healthcare are endless. Patients can expect more comprehensive monitoring capabilities, improved diagnostics, and tailored treatment plans. Healthcare providers will have access to real-time data, enabling them to make informed decisions and deliver precise care.
| Advancements | Possible Impact |
|---|---|
| Integration of AI and predictive analytics | Personalized treatment plans and interventions |
| Expansion of the IoMT | Seamless data exchange and collaboration |
| Comprehensive health monitoring capabilities | Early detection and prevention of health issues |
Conclusion
Personal health devices integrated into Personal Area Networks (PANs) are revolutionizing health monitoring and management. The seamless integration of wearable sensors with smartphones enables continuous data collection and remote monitoring, empowering individuals to take control of their health like never before.
As technology continues to advance, personalized healthcare will become more accessible, providing individuals with the tools they need for early detection and prevention of health issues. The future holds promising trends in PAN integration, including the widespread adoption of wireless monitoring and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
PAN integration allows for the seamless exchange of health-related data between personal health devices, healthcare providers, and researchers. This enables real-time monitoring, accurate diagnoses, and personalized treatment plans. By harnessing the power of predictive analytics and artificial intelligence, personalized healthcare will be optimized, ensuring tailored interventions and improving patient outcomes.
Looking ahead, the potential for PAN integration, predictive analytics, and the IoMT in the field of personal health devices is vast. These technologies will pave the way for a new era of personalized and proactive healthcare, transforming the way we monitor and manage our well-being.
FAQ
What are personal health devices and their integration into Personal Area Networks (PANs)?
Personal health devices refer to wearable sensors and other devices used for monitoring vital signs and physical activity. These devices are integrated into Personal Area Networks, allowing for seamless communication with smartphones and the transmission of health data to a centralized system.
What are the benefits of mHealth and wireless personal health monitoring?
mHealth, or mobile health, leverages advancements in technology to enable continuous monitoring of vital signs and physical activity. This provides users with real-time health information, allows for accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and aids in population health management and research.
What role do wearable sensors and smartphones play in personal health monitoring?
Wearable sensors collect data on vital signs and physical activity, while smartphones act as the central hub for data collection, processing, and communication. They connect wirelessly to the sensors, collect the data, and transmit it to a cloud or a centralized system. This enables remote monitoring and informed decision-making by healthcare providers.
What does the future hold for personal health devices and PAN integration?
Advancements in artificial intelligence and predictive analytics will enable personalized healthcare based on patient data analysis. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) will connect personal health devices to larger healthcare systems, facilitating data exchange and collaboration. PAN integration will continue to evolve, providing users with more comprehensive health monitoring capabilities for preventive and proactive healthcare.
What can we expect from personal health devices and PAN integration in the future?
Personal health devices integrated into PANs offer significant advantages in health monitoring and management. As technology advances, personalized healthcare, early detection, and prevention of health issues will become more accessible. Future developments include predictive analytics, artificial intelligence, and further integration of the Internet of Medical Things, paving the way for a new era of personalized and proactive healthcare.