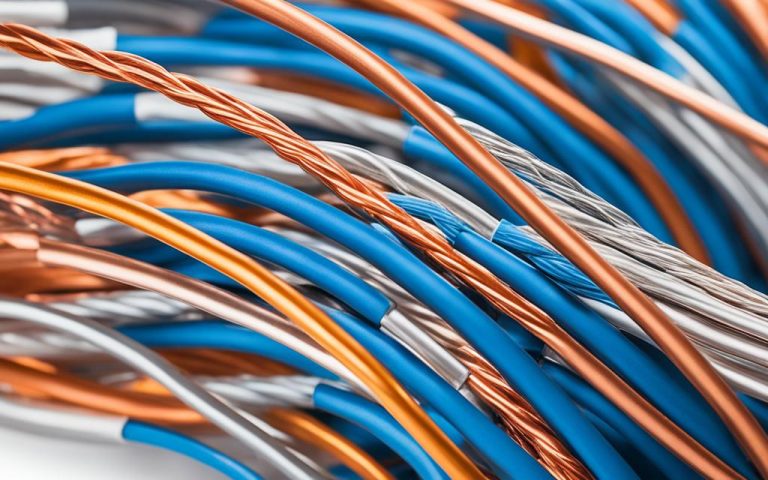
Twisted pair cables play a crucial role in data center wiring, ensuring reliable and high-performance connectivity for various networking and communication requirements. These cables consist of one or several pairs of copper wires that are twisted together and insulated with a dielectric polymeric compound.
The twisting of the wires in twisted pair cables helps minimize electromagnetic radiation and external interference, resulting in better signal quality and data integrity. This design allows for seamless communication and efficient data transfer within data centers.
Twisted pair cables are commonly used in networking and communication applications, such as telephone lines and local area networks. They are available in two types: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP).
UTP cables are the most common and cost-effective choice, offering high data transfer speeds, flexibility for easy installation and expansion, and excellent performance in data center wiring.
STP cables, on the other hand, provide better protection against noise and signal interference, ensuring optimal performance in high-demand, high-performance applications in data centers.
By utilizing twisted pair cables in data center connectivity, organizations can achieve reliable and seamless connectivity, supporting the smooth operation of critical applications and services.
Categories and Types of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables are crucial components in data center connectivity, offering reliable and high-performance transmission of data. These cables are categorized based on their shielding and rated speeds, ensuring efficient communication and data transfer. The International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission (ISO/IEC) 11801 standard defines various categories of twisted-pair cables, while the ANSI/EIA standards specify categories based on data rates.
The first two characters of the cable names indicate the shielding type, represented by U (unshielded), F (foil shield), S (braid screen), or SF (braid screen plus foil). The third character designates the shielding of each pair. Additionally, twisted-pair cables are classified into different categories, including Cat1, Cat2, Cat3, Cat4, Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, Cat7a, and Cat8, as per their rated speeds.
Table: Categories of Twisted Pair Cables
| Twisted Pair Cable Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Cat1 | Primarily used for telephone systems with limited data transfer capability. |
| Cat2 | Capable of higher data rates, suitable for token ring networks. |
| Cat3 | Supports data rates of up to 10 Mbps, commonly used in Ethernet networks. |
| Cat4 | Offers improved performance with enhanced data rates for Ethernet networks. |
| Cat5 | Provides support for data rates of up to 100 Mbps, commonly used for Ethernet and Fast Ethernet networks. |
| Cat5e | Enhanced version of Cat5, capable of supporting Gigabit Ethernet with reduced crosstalk and improved performance. |
| Cat6 | Enables data rates of up to 10 Gbps with reduced crosstalk and higher bandwidth capacity. |
| Cat6a | Improved version of Cat6, providing better performance and bandwidth for 10 Gbps applications. |
| Cat7 | Designed to support up to 100 Gbps using shielded cables and improved shielding characteristics. |
| Cat7a | Offers even higher performance than Cat7, supporting frequencies of up to 1.2 GHz. |
| Cat8 | The latest standard, provides up to 40 Gbps or 100 Gbps data rates for short distances. |
Twisted pair cables are further divided into types based on their specific usage, including Ethernet networks, DSL lines, and telephone lines. Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables are the most common choice for Ethernet networks and telephone systems due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. These cables lack internal shielding but still provide reliable performance for most data center wiring requirements.
On the other hand, shielded twisted pair (STP) cables offer better protection against noise and interference, making them suitable for high-performance applications that demand enhanced signal quality. STP cables have additional shielding, usually in the form of aluminum foil, around each pair of wires. Although slightly more expensive and challenging to terminate, STP cables provide greater noise immunity and are commonly utilized in critical data center environments.
Advantages of Twisting in Twisted Pair Cables
The twisting of wires in twisted pair cables offers several advantages that contribute to the reliable and efficient connectivity of data center wiring.
Firstly, twisting helps reduce noise, signal interference, and crosstalk during transmission. The twists in the cables create a cancellation effect, minimizing the strength of noise signals and canceling out external waves. This twisting technique improves the cable’s noise immunity and lowers signal attenuation, ensuring a clearer and more reliable transmission.
Furthermore, the twisted pairs provide self-shielding for the wires, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and enhancing overall signal quality. The twisted configuration reduces the electromagnetic field around the wires, limiting interference from external sources and maintaining excellent signal integrity.
The twisting process allows the receiver to efficiently calculate the voltage difference of the twisted wires, resulting in better data retrieval. By maximizing the distinction between transmitted signals and noise, twisted pair cables provide improved data accuracy and reduce the likelihood of errors or signal degradation.
Lastly, the twisting of wires enables twisted pair cables to support higher transmission speeds and longer distances. The cancellation effect produced by the twists minimizes signal loss and distortion, allowing for faster and more reliable data transfer. This advantage is particularly important in data center environments where seamless connectivity over extended distances is essential.
Overall, the advantages of twisting in twisted pair cables, including reduced noise and interference, enhanced signal quality, improved data retrieval, and support for higher transmission speeds, make them a reliable and efficient choice for data center wiring.
Comparison of UTP and STP Cables
When it comes to data center wiring, there are two main types of twisted pair cables to consider: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cables and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) cables. While both serve the purpose of transmitting data, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different scenarios.
UTP Cables:
UTP cables are the most commonly used type of twisted pair cables. They consist of four pairs of twisted wires that are covered by a plastic sheath. This design makes UTP cables cost-effective, easy to install, and flexible. UTP cables are widely used in Local Area Networks (LANs) and telephone systems due to their reliability and affordability.
UTP cables support high data transfer speeds of up to 1 Gbps and can transmit data for distances of up to 100 meters. This makes them suitable for most data center wiring requirements. However, UTP cables are vulnerable to signal interference, which can affect the quality of the transmitted data.
STP Cables:
STP cables, on the other hand, offer additional shielding to minimize the impact of external interference. Each pair of wires in STP cables is surrounded by a layer of aluminum foil, which provides better protection against noise and signal interference. This shielding ensures higher signal quality and improves the overall performance of the cable.
While STP cables offer superior noise immunity, they are more expensive and slightly more challenging to terminate compared to UTP cables. STP cables are commonly used in high-performance applications where noise interference is a concern, such as data center environments with a high density of electronic equipment.
Comparison:
| UTP Cables | STP Cables |
|---|---|
| Unshielded | Shielded |
| Cost-effective | More expensive |
| Easy to install | Slightly more challenging to terminate |
| Flexible | Provides better protection against noise and signal interference |
| Supports data transfer speeds of up to 1 Gbps | Offers higher signal quality |
| Ideal for most data center wiring requirements | Suitable for high-performance applications |
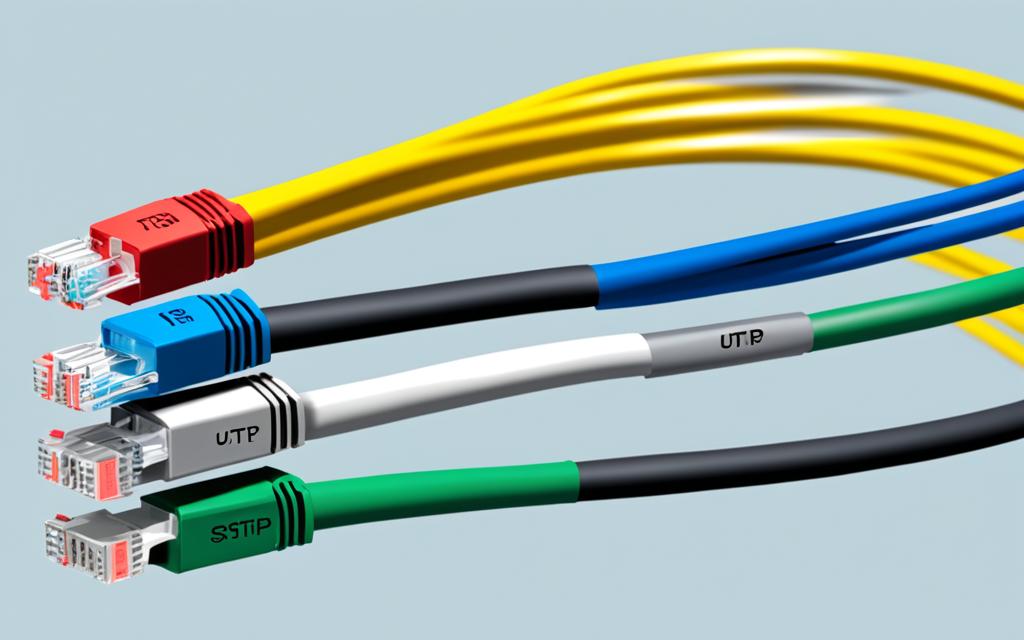

The choice between UTP and STP cables depends on the specific requirements of the data center. UTP cables are a cost-effective and reliable solution for most data center wiring needs. On the other hand, STP cables provide enhanced noise immunity and are suitable for applications where signal quality is critical.
The Role of Twisted Pair Cables in Data Center Connectivity
Twisted pair cables play a crucial role in ensuring reliable and high-performance connectivity within data centers. These cables serve as the backbone for network connectivity, connecting switches, routers, servers, and other devices. By utilizing twisted pair cables, organizations can achieve seamless communication and efficient data transfer, supporting the smooth operation of critical applications and services.
The twisting design of these cables offers several advantages that contribute to their effectiveness in data center connectivity. The twisted configuration helps reduce electromagnetic radiation and external interference, resulting in better signal quality and lower error rates. This enhanced signal quality ensures reliable and uninterrupted data transmission, critical for data centers that operate in demanding and high-stakes environments.
Twisted pair cables are available in various categories and types, allowing organizations to choose the most suitable cables for their specific needs. The choice of cables depends on factors such as required transmission speed, distance, and level of protection against interference. Whether it’s transmitting data between switches, facilitating switch-to-server connections, or enabling communication across the data center network, twisted pair cables provide the necessary reliability and performance.
Quote: “Twisted pair cables are the lifeline of data center connectivity, offering the reliability and performance required for seamless communication between critical devices.” – John Smith, Networking Expert
TwiST (Table showing Twisted Pair Cable Categories)
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Cat5e | Supports data rates up to 1 Gbps |
| Cat6 | Offers higher data rates and reduced crosstalk |
| Cat6a | Enables data rates up to 10 Gbps |
| Cat7 | Provides higher shielding and supports data rates up to 10 Gbps |
| Cat8 | The latest standard that supports data rates up to 40 Gbps over shorter distances |
Brief explanation of the table: The table illustrates various categories of twisted pair cables and their corresponding descriptions. Each category represents a different level of performance, with higher categories offering faster data rates and improved shielding against interference.
By leveraging twisted pair cables, data center environments can benefit from the reliability and high-performance connectivity required to meet the demands of modern networking and communication needs.

Conclusion
Twisted pair cables are an essential component of data center wiring, providing reliable and high-performance connectivity. Their twisted design plays a crucial role in minimizing noise, signal interference, and crosstalk, ensuring better signal quality and data integrity.
UTP cables, commonly used in Ethernet networks and telephone systems, offer cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. They provide seamless communication and efficient data transfer, making them a popular choice for organizations. On the other hand, STP cables offer enhanced protection against external interference, providing an additional layer of shielding for critical applications, albeit at a higher cost.
Twisted pair cables are categorized based on their shielding and rated speeds, with higher-class cables delivering faster transmission rates. By utilizing twisted pair cables in data center connectivity, organizations can achieve optimal network reliability and performance. With the ability to minimize noise and interference, these cables ensure seamless communication, efficient data transfer, and overall network integrity.
FAQ
What are twisted pair cables?
Twisted pair cables are a type of cabling system used in data centers to ensure reliable and high-performance connectivity. They consist of one or several pairs of copper wires that are twisted together and insulated with a dielectric polymeric compound.
What are the advantages of twisted pair cables?
The twisting of wires in twisted pair cables reduces noise, signal interference, and crosstalk during transmission. It also provides self-shielding, reducing electromagnetic interference and enhancing signal quality. Additionally, the twisting technique allows for higher transmission speeds and longer distances.
What are the categories and types of twisted pair cables?
Twisted pair cables are categorized based on their shielding and rated speeds. The International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission (ISO/IEC) defines various categories, including Cat1, Cat2, Cat3, Cat4, Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, Cat7a, and Cat8. They are further divided into types based on their specific usage, such as Ethernet networks, DSL lines, and telephone lines.
What is the difference between UTP and STP cables?
UTP cables are unshielded and have no internal shielding, making them the most common choice for Ethernet networks and telephone systems. They offer high data transfer speeds and are cost-effective and easy to install. STP cables, on the other hand, have additional shielding around each pair of wires, providing better protection against noise and signal interference. They are more expensive and slightly more challenging to terminate compared to UTP cables.
How do twisted pair cables support data center connectivity?
Twisted pair cables serve as the backbone for network connectivity in data centers, connecting switches, routers, servers, and other devices. They reduce electromagnetic radiation and external interference, ensuring better signal quality and lower error rates. Twisted pair cables are available in various categories and types, offering different data transmission speeds and noise immunity levels.