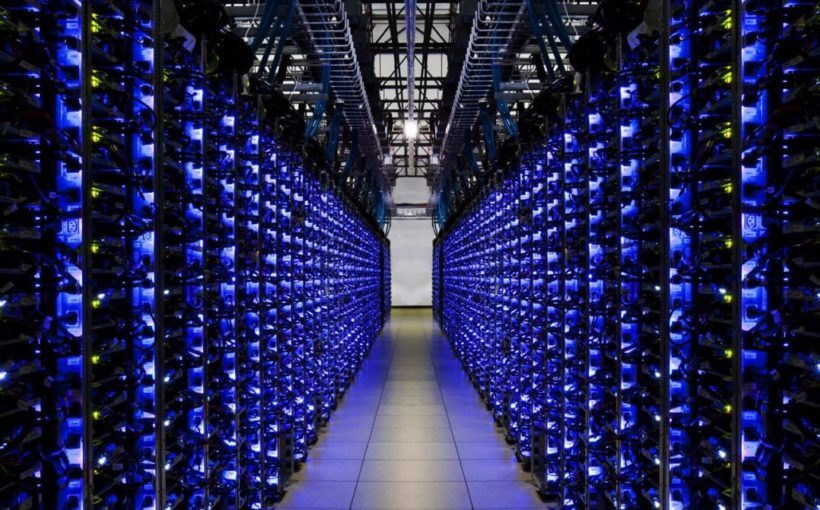
This trilogy of articles seems to be on the growth of larger and higher information centres internationally. It considers what’s driving this building growth, among the challenges it faces and examples of how it’s being applied. For numerous years the excitement phrase within the IT business has been “cloud”. The phrase represents a shift in approach all of us entry and perform our computing wants with an elevated reliance on the web. The time period has even crossed into mainstream parlance due to companies equivalent to Apple’s iCloud.
The concept behind cloud computing is that customers can entry computing assets, equivalent to purposes or cupboard space, on distant computer systems, by way of the web relatively than on native particular person machines. The benefits are plentiful as shoppers can entry simply the companies they want as and once they want them (akin to conventional utilities) and from a large number of units and places. Many people use explicitly labelled cloud companies however the majority of these used, significantly within the personal market, do not essentially immediate the identical recognition. For instance, the massively standard social media instruments, Twitter and Fb, permit us to share communications and media by storing it on distant servers the place it may be accessed by anybody with whom we want to share it by way of the web, i.e., via the cloud. In a way, cloud computing is a pure evolution of the idea of the world large internet, which was supposed to offer a community of shared paperwork, nevertheless with the large availability of upper bandwidth web connections and the adoption of Internet 2.0, together with the thought of person generated content material, the previous easy paperwork have developed into advanced internet primarily based purposes and wealthy media. The pliability, scalability and price effectiveness of cloud computing affords appreciable advantages for each personal and enterprise shoppers in comparison with ‘conventional’ one-off installations on particular person units and subsequently adoption charges proceed to rise. The ideas can seem pretty ephemeral to the buyer, as they entry all of their computing useful resource by way of the web however, in the end, all of that digital info does must be saved someplace. Because the companies get an increasing number of standard, so social community suppliers, cloud storage suppliers, cloud utility suppliers and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) suppliers want to seek out an increasing number of bodily capability and up to date years have subsequently seen what has been described by some as an information centre arms race to construct extra and larger information centre services. The wrestle subsequently for information centre suppliers is to construct greater, to succeed in the capability they want, however on the identical time, minimise the ability that they devour and the influence that they’ve on the encircling setting. Energy consumption is measured by a PUE (Energy Utilization Effectiveness) rating which signifies the power consumed by supporting infrastructure (primarily warmth administration) versus that required to energy the core servers. The business benchmark is a PUE rating of two.Zero which represents one unit of energy consumed on infrastructure for each one on servers, while the final word effectivity can be a PUE of 1. Not solely does a extra environment friendly facility show greener and extra sustainable however, for the supplier, it minimises value and will increase the scope for elevating capability. Consequently information centre constructors are more and more seeking to new and progressive methods to carry this rating under 2 and as near 1 as potential.
The next installments of this trilogy of articles seems to be on the scale of among the largest information centres on this planet for instance how the necessity for digital information storage has modified the panorama of business complexes all over the world.