Fiber optic cables are the lifeline of modern telecommunications and data networking, providing high-speed connectivity for businesses and individuals alike. However, these cables are not impervious to damage and can experience cuts or other forms of damage that disrupt the seamless flow of data. In such cases, swift and effective fiber optic cable repair techniques are essential to restore uninterrupted connectivity and prevent potential losses for businesses.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the necessary knowledge and techniques for repairing cut or damaged fiber optic cables, ensuring the restoration of high-speed connectivity. Whether you’re a professional network technician or a DIY enthusiast, understanding the intricacies of fiber optic cable repair is vital in maintaining a reliable and efficient network.
Understanding Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cables are revolutionizing data transmission with their high-speed and efficient communication capabilities. These cables play a crucial role in transporting vast amounts of data over long distances with minimal signal loss. By utilizing the principles of light transmission, fiber optic cables have become the backbone of modern telecommunications and are widely used in various industries, including telecommunications, internet services, and data centers.
The working principle of fiber optic cables is based on the transmission of light signals. The core of the cable carries the light signals, while the cladding surrounding the core reflects them to ensure that the signals stay within the cable. This unique configuration allows for the transmission of large amounts of data at incredible speeds.
The use of light signals in fiber optic cables enables faster data transmission compared to traditional copper cables. With the ability to carry data over long distances without significant signal degradation, fiber optic cables have become the preferred choice for high-bandwidth applications and long-haul communications.
To protect the delicate internal components, fiber optic cables are encased in a protective jacket. This jacket acts as a barrier against physical damage, moisture, and other environmental factors that could impact the cables’ performance and longevity.
Understanding the composition and working principle of fiber optic cables is essential for effective repair and troubleshooting. By having a grasp of how these cables function and transmit data, technicians can identify and address any issues that may arise during installation, maintenance, or repair processes.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables offer several advantages over traditional copper cables:
- High-Speed Data Transmission: Fiber optic cables can transmit data at speeds exceeding several terabits per second, enabling faster and more efficient communication.
- Large Bandwidth Capacity: These cables have a much higher bandwidth capacity than copper cables, allowing for the transmission of vast amounts of data simultaneously.
- Long-Distance Communication: Fiber optic cables can carry data over significantly longer distances without signal degradation, making them ideal for long-haul communications.
- Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference: Unlike copper cables, fiber optic cables are not affected by electromagnetic interference, ensuring a more reliable and secure connection.
- Lightweight and Compact Design: Fiber optic cables are thinner and lighter than copper cables, making them easier to install and manage in various environments.
The advantages offered by fiber optic cables make them the preferred choice for high-speed and high-bandwidth applications, including internet connectivity, telecommunication networks, video streaming, and cloud computing.
Fiber Optic Cable Structure
A typical fiber optic cable consists of three primary components:
- Fiber Core: The fiber core is the innermost part of the cable, through which the light signals are transmitted. It is made of a high-purity glass or plastic material that has excellent light transmission properties.
- Fiber Cladding: Surrounding the fiber core is the fiber cladding, which is made of a different type of glass or plastic. The cladding has a slightly lower refractive index than the core, allowing it to reflect the light signals back into the core, preventing signal loss.
- Protective Jacket: The fiber core and cladding are enclosed within a protective jacket, which provides mechanical strength and protects the internal components from damage due to bending, tension, moisture, and other environmental factors.
The precise construction and composition of fiber optic cables may vary depending on the specific application and industry requirements.
Common Causes of Fiber Optic Cable Damage
Fiber optic cables are highly susceptible to damage from various factors. Understanding these common causes is crucial for implementing preventive measures that ensure the durability and reliability of the cables.
Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions play a significant role in fiber optic cable damage. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can cause the cable materials to degrade over time. High humidity levels contribute to increased moisture ingress into the cable, leading to corrosion and signal loss. Exposure to water or corrosive substances can weaken the protective jacket and compromise the integrity of the optical fibers.
Mechanical Stress
Mechanical stress is another common cause of fiber optic cable damage. During installation, maintenance, or accidental mishandling, cables may experience bending, twisting, or pulling forces that can result in microbends or macrobends. These bends disrupt the flow of light signals through the fiber, leading to signal loss or degradation. Proper cable management and handling techniques are crucial to mitigating mechanical stress and preserving the cable’s longevity.
Human Error
Human error is yet another factor contributing to fiber optic cable damage. Improper termination of fibers, such as incorrect alignment or inadequate securing, can introduce signal loss points. Accidental cuts or damage caused by careless handling or insufficient training can also disrupt the cable’s functionality. Strict adherence to best practices and comprehensive training programs are key to minimizing human-induced cable damage.
Overall, being aware of the environmental factors, mechanical stress, and human error enables technicians and network operators to take proactive measures to prevent fiber optic cable damage and ensure optimal performance.
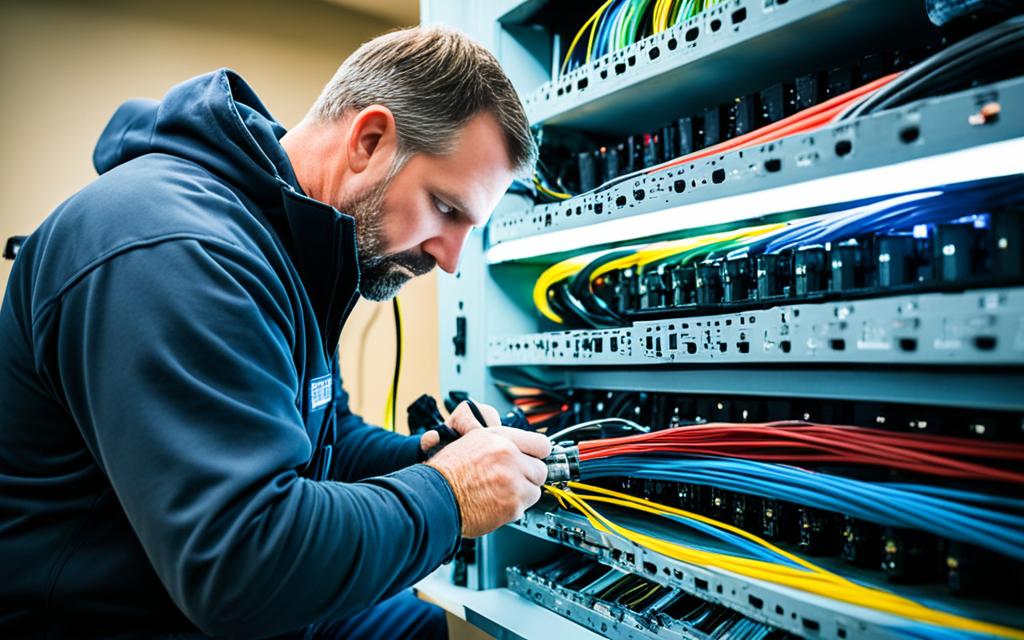
Steps to Repair a Cut or Damaged Fiber Optic Cable
Repairing a cut or damaged fiber optic cable involves a systematic process that ensures the restoration of optimal signal transmission. By following these step-by-step instructions, you can effectively repair your fiber optic cable and minimize downtime.
- Identify the damaged area: Begin the repair process by visually inspecting the cable for any visible cuts or damage. Alternatively, you can use an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) to pinpoint the precise location of the damage.
- Gather necessary tools: Before proceeding with the repair, ensure you have the necessary tools at hand. These tools may include a fusion splicer, fiber cleaver, and fiber stripper. Having all the required tools ready will streamline the repair process.
- Prepare the fiber ends: To initiate the repair, strip off the protective jacket from the damaged area of the cable. Next, clean the exposed fiber ends using lint-free wipes and fiber optic cleaning solution. This step ensures proper fusion or connection of the fibers.
- Choose the repair method: Depending on the severity and nature of the damage, you can choose between fusion splicing, connectors, or mechanical splices for repairing the fiber optic cable.
- Fusion splicing: In this method, the damaged fibers are aligned and fused together using a fusion splicer. Fusion splicing ensures a low-loss connection and is ideal for permanent repairs.
- Connectors: Using connectors involves attaching pre-polished connectors to the fiber ends. This method provides flexibility and ease of installation, making it suitable for temporary or quick repairs.
- Mechanical splices: Mechanical splices bring the fibers into alignment and hold them securely using metallic sleeves or adhesive. This method is cost-effective and can be used for both permanent and temporary repairs.
Once the repair method is selected, ensure that the repaired area is protected and secured using appropriate strain relief techniques and protective enclosures. Finally, test the repaired cable to verify its performance and ensure the restoration of high-speed connectivity.
Tips for Successful Fiber Optic Cable Repair
When it comes to fiber optic cable repair, attention to detail and adherence to best practices are crucial for success. Here are some essential tips to ensure a seamless repair process:
Cleaning and Inspection: Before starting the repair, thoroughly clean and inspect the ends of the cable. Any dirt, dust, or contaminants can affect the quality of the repair. Use lint-free wipes and isopropyl alcohol to clean the fiber ends and ensure they are free from any debris.
High Precision Fiber Cleavers: Invest in high precision fiber cleavers, such as those offered by Fujikura or Sumitomo. These cleavers provide clean and precise cuts, ensuring optimal splicing and minimizing signal loss. Regularly maintain and calibrate your fiber cleavers to maintain their accuracy.
Quality Testing and Verification: After the repair is complete, perform quality testing and verification to ensure the integrity of the repaired cable. Use equipment such as Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDRs) to measure the optical loss and detect any potential issues. This step is essential in guaranteeing that the repaired cable meets the required specifications and provides reliable performance.
By following these tips, you can enhance the effectiveness and reliability of your fiber optic cable repairs. Remember to always prioritize cleaning, invest in high-quality fiber cleavers, and perform thorough testing and verification to ensure optimal results.
FAQ
What are fiber optic cables?
Fiber optic cables are high-speed and efficient communication cables that use light signals to transmit information. They consist of a core, cladding, and protective jacket.
How can fiber optic cables be damaged?
Fiber optic cables can be damaged by environmental factors like extreme temperatures and humidity, mechanical stress from bending and twisting, and human error such as accidental cuts.
How do I repair a cut or damaged fiber optic cable?
The repair process involves identifying the damaged area, gathering the necessary tools such as a fusion splicer and fiber cleaver, preparing the fiber ends, and then either fusion splicing the fibers or using connectors or mechanical splices.
What should I consider for successful fiber optic cable repair?
Successful fiber optic cable repair requires proper cleaning and inspection of the cable ends, using high precision fiber cleavers, and performing quality testing and verification to ensure the integrity of the repaired cable.