In the fast-changing world of cryptocurrency, pegging is key. It helps keep things stable and links the new with the old. This article explores what pegging means in the crypto space and why it’s important.
So, what is pegging in crypto? It’s about connecting the value of a digital asset to something more stable. For example, tying a cryptocurrency’s value to a fiat currency. This link boosts trust in cryptocurrencies, which can be wild and hard to predict.
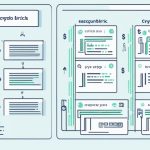
Crypto pegging uses different ways to work, like having backed reserves. Here, a stable asset is kept as a guarantee for the pegged cryptocurrency. This makes users more confident, knowing the pegged digital asset is supported by something tangible.
One well-known pegged asset is Tether (USDT), a stablecoin tied to the US dollar. Every USDT equals one US dollar. This stable value helps it be trusted for trading and storing value in the crypto world.
Crypto pegging is very important. It brings stability to the crypto market, which makes it more attractive to a broad range of people. It also helps connect crypto with traditional finance. This connection encourages more people to use and accept cryptocurrencies.
As crypto keeps growing, pegging will likely grow more important. Knowing what pegging is and why it matters is key to exploring the new and changing world of cryptocurrencies.
What Does Pegging Mean in Crypto?
In the crypto world, pegging means tying a cryptocurrency’s value to an external asset or currency. This practice is used to make the crypto market more stable and less volatile. For instance, a cryptocurrency could be tied in value to a fiat currency like the US dollar or to a commodity like gold.
Linking a cryptocurrency’s value to that of another in economics is known as pegging. But in cryptocurrencies, it’s different. With crypto pegging, we gain control and transparency using smart contracts and decentralized methods.
Pegged cryptocurrencies offer a steady value and aim to lessen big price changes. This stability makes them good for buying things daily or as an investment. With the crypto tied to a dependable external asset, people trust its value and use.
Cryptocurrencies like Tether (USDT) are pegged to the US dollar, while Digix Gold (DGX) is pegged to the value of one gram of gold. These pegs let people buy and save their money without dealing with the ups and downs of other cryptos.
Using pegging in crypto needs a lot of thought. We must be sure the peg stays reliable and that the backing for the crypto’s value is safe and clear. Still, when done well, pegging can make crypto a more stable place.
The table below illustrates some popular pegged cryptocurrencies:
| Cryptocurrency | Pegged Asset |
|---|---|
| Tether (USDT) | US Dollar |
| DAI | USD |
| Paxos Standard (PAX) | USD |
| Digix Gold (DGX) | Gold |
| USD Coin (USDC) | USD |
These examples show the many different assets to which cryptocurrencies can be tied. People have a variety of choices based on what they prefer or need.
The Importance of Crypto Pegging
In the world of cryptocurrency, everyone wants stability. Crypto pegging helps achieve this. It acts as an anchor in the ever-changing crypto market.
Pegging links a cryptocurrency’s value to an outside asset. This asset can be a fiat currency or a commodity. The goal is to keep the cryptocurrency’s value steady, unlike other digital assets that fluctuate often.
This steady value offers benefits to those in the market. It lessens the market’s usual ups and downs. So, pegged cryptocurrencies are more dependable for storing value.
Because of this, people can use these currencies for buying things. They don’t have to worry about losing value suddenly.
Moreover, pegged cryptocurrencies make the market more trustworthy. More people are likely to join, leading to wider usage. This trust is key for the crypto world to mature. It shows that cryptos are more than just risky investments.
Interested to learn more about pegging in crypto? Visit these sites: Investopedia, PrimeXBT, and Gate.io.
FAQ
What is pegging in the context of cryptocurrency?
Pegging in cryptocurrency means linking a digital asset’s value to another asset, like a fiat currency. It’s done to add stability and decrease volatile changes common with cryptocurrencies.
How does pegging work in the crypto world?
In the crypto world, pegging creates a cryptocurrency with a fixed value connected to another stable asset, often the US dollar. This involves keeping a fixed value through means like collateral or algorithms.
How is pegging in crypto different from traditional pegging in economics?
In economics, pegging usually refers to fixing a currency’s value to another currency or set of currencies. In crypto, it’s about tying a digital asset’s value to another currency or asset, using blockchain to ensure stability.
Can you provide some examples of pegged cryptocurrencies?
Sure! Examples include Tether (USDT), pegged to the US dollar. There’s also Dai (DAI), which tracks the US dollar on the Ethereum blockchain. Binance USD (BUSD) mirrors the US dollar and is from the Binance exchange.
What is the importance of pegging in the cryptocurrency market?
Pegging is crucial in crypto to give investors and traders a stable choice. It lowers the extreme value changes seen in crypto. This makes pegged cryptos appealing for those wanting more security.
What are the benefits of using pegged cryptocurrencies?
Using pegged cryptos can mean less volatility, making them ideal for daily use or saving. They offer a stable option since their value is connected to a known asset. Plus, they help with global payments and hedge against inflation.
Are there any risks associated with pegged cryptocurrencies?
Yes, there are risks. Poor reserve handling and lack of transparency can shake faith in the peg’s stability. Also, because they’re tied to fiat currencies, they face regulatory threats.
How important is proper reserve management for pegged cryptocurrencies?
Reserve management is vital for pegged cryptos to stay secure. The pegged currency issuer must show they have enough reserves for their tokens. This trust in the system prevents sudden value drops.