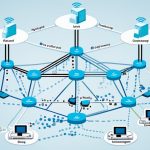
Wide Area Network (WAN) connects far-off places. It uses different topologies like point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, full mesh, ring, and star. Each has its own benefits.
When picking a WAN topology, teams look at many things. They think about how much data needs to move and how fast1. They check what apps are used and how much data is sent1.
Choosing the right network design is key. Topologies like point-to-point and mesh offer different perks2. Mesh keeps networks running even if one link breaks2. But, physical damage can still cause problems2.
Keeping data safe is a big deal in WAN design. Using encryption and firewalls helps protect data1. It’s important to have many security layers1.
Quality of Service (QoS) makes sure important apps work well. It helps with things like video calls by making them a priority1.
Having backup plans is key to keep networks running smoothly. Redundant links and failovers help avoid downtime1.
In summary, picking the right WAN topology means looking at many things. You need to think about how much data moves, the network design, security, QoS, and backups. By doing this, teams can build strong WANs that fit their needs.
Key Takeaways
- Bandwidth needs are based on how people use the network, what apps they use, and how much data they send1.
- Network design matters, with mesh offering redundancy and physical topologies having risks2.
- Security is key with things like encryption and many security layers1.
- QoS makes sure important apps run smoothly with special rules1.
- Redundancy and failovers cut down on downtime and single points of failure1.
Point-to-Point Topology
Point-to-point topology is a common WAN (Wide Area Network) setup. It lets two far-off sites exchange Ethernet frames directly. This setup creates a direct link between two places, making data transfer efficient and secure.
It can be done with dedicated leased lines or Metro Ethernet (MetroE) services. Dedicated leased lines give a private link between sites. They offer lots of bandwidth and are great for important tasks and big data needs.
Metro Ethernet uses current Ethernet networks for point-to-point links. Telecom providers offer these services. They let companies connect without needing special leased lines. Metro Ethernet is affordable and can grow with your needs.
Point-to-point topology has many benefits, including:
- Enhanced security: The link is only for the two sites, lowering the chance of hackers or data theft.
- Reliable performance: A direct connection means steady bandwidth and dependable performance for smooth data flow.
- Minimal latency: These connections are fast, making real-time talks and quick data sharing possible.
But, it’s not all good. Setting up and keeping dedicated leased lines can be pricey, especially for long distances. If one site goes down, the link between them could break until fixed.
In summary, point-to-point topology is a strong way to link two distant sites. It uses leased lines or Metro Ethernet to create secure, fast connections tailored to your needs.
Point-to-Multipoint Topology
The point-to-multipoint WAN topology is a key choice for connecting devices efficiently. It uses a central site as the hub to talk to many remote sites. This forms a network that looks like a star.
This setup lets the central site send data to the remote sites but not the other way around. This makes sending data fast and suits many business needs.
Choosing this network type has big benefits. It makes managing the network easier and lets it grow bigger. The central site controls everything, making it simpler to keep the network running smoothly.
The central site is very important in this network. It sends out important info to all the remote sites. This keeps everything running the same way across the network.
“OMP protocol is responsible for establishing and maintaining Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN control plane.”
3
OMP is key to the control plane in Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN. It helps set up and keep the network running. OMP sends important info from the central site to all the edge devices.
“OMP advertises routes and learned services to peers using OMP routes and transport location mappings.”
3
OMP helps the hub share routes and services with other devices. It uses OMP routes and mappings to spread the word. This keeps all devices updated on the network’s routes.
OMP also works with OSPF and BGP for better routing in the network. This makes sure data moves fast and finds the best path.
“TLOC routes identify transport locations with attributes like private and public addresses, carrier type, color, and preference.”
3
TLOC routes are crucial for finding and connecting to transport locations. They give detailed info about these locations. This helps network managers control how data moves based on certain rules.
TLOC routes also help keep the network stable by using fixed IP addresses. This makes the network more reliable and improves its performance.
When picking a network type, point-to-multipoint is a strong choice. It offers centralized control, easy management, and can grow with your needs. It makes sending data fast and connects many remote sites well.
In short, the point-to-multipoint WAN topology is a smart pick for businesses. It has centralized control and makes managing the network easy. This setup supports fast data transfer and growth in various industries.
Full Mesh Topology
The full mesh topology connects all devices in a wide area network (WAN) directly, making a highly connected network. Each device links to every other, so there’s no need for a central hub. This is great for situations needing high redundancy and fault tolerance4.
For Ethernet LAN (E-LAN) services, the full mesh topology is a big win. It lets devices talk directly, speeding up data transfer and cutting down on delays. Without a central hub, the network is less likely to fail, making it more reliable. Adding new devices is easy, without messing up the network4.
Benefits of Full Mesh Topology
The full mesh WAN topology has many benefits for organizations:
- Robust Communication: Every device can talk to any other, making data transfer efficient and reliable. This cuts down on delays and boosts network speed4.
- High Fault Tolerance: It’s the most fault-tolerant network type. If a device fails, others can still connect, keeping communication smooth and minimizing downtime4.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Adding new devices is easy without disrupting the network. This is great for companies with changing needs4.
Cisco’s Catalyst SD-WAN solution is a perfect match for the full mesh topology. It brings together routing, security, policy, and orchestration for big networks. This lets companies use SD-WAN’s benefits like easy network management, flexibility, strong security, and cloud connectivity5.
| Comparison of WAN Topologies | |
|---|---|
| Topology | Advantages |
| Full Mesh | High fault tolerance Robust communication capabilities Scalability and flexibility |
| Point-to-Point | High security Simplicity and cost-effectiveness |
| Point-to-Multipoint | Efficient bandwidth utilization Reduced deployment costs |
| Ring | Unidirectional data flow Redundancy and fault tolerance |
| Star | Centralized management and control Easy troubleshooting |
Ring Topology
A ring topology connects devices in a circle, making it a closed loop. It’s called a ring because of its shape. Data moves around the network in one direction, going through each device before it reaches its destination. This setup has pros and cons, making it good for some situations.
One big plus of a ring topology is how it handles faults. If there’s a problem or a break in the ring, data can find another way, keeping communication going. This is thanks to redundancy, where devices talk to two others directly.
Ring topologies also give all computers equal access to the network. Everyone can send and receive data without bias, making communication fair. This setup also helps in checking for errors and sending back confirmations, making the network work better.
But, ring topologies have some downsides. For one, data can only move in one direction, which can slow things down if it has to go through many devices. This limits how fast and big the network can be compared to other setups.
Also, a single issue in the ring can shut down the whole network. If a device or link fails, the network gets cut off. While it can reroute data, fixing the problem quickly is key to keep things running smoothly.
Ring topologies used to be common in LANs but are less so today for fast networks. Yet, they can still be a good choice for WANs, like linking remote sites to a main office.
Star Topology
The star topology is a common network setup in WAN (Wide Area Network) designs. It connects many nodes to a central hub, creating a star shape. This central hub is where all communication goes through, making it easy to manage the network.
This setup is different from point-to-point or full mesh topologies because it needs a central hub. This hub connects to all devices in the network.
Adding new devices to the star topology is easy because they connect directly to the central hub. This makes it great for growing companies or those often changing their network setup.
Each device in the star topology connects directly to the central hub. If one device fails, it won’t stop the others from working. This makes the network more reliable and less likely to have a single point of failure.
The central hub is where the network is managed and monitored. This makes fixing problems and keeping the network running smoothly easier.
Advantages of Star Topology:
- Easy network integration and scalability
- Enhanced network reliability
- Efficient management and administration
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
- Dependence on the central hub: If the central hub fails, the entire network may be affected
- Higher implementation and maintenance costs compared to other topologies
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Easy network integration and scalability | Dependence on the central hub |
| Enhanced network reliability | Higher implementation and maintenance costs |
| Efficient management and administration |
Real-Life Star Topology Example
“A prime example of a star topology in action is the corporate network of ABC Corporation. With branches across many locations, ABC Corporation uses a central hub at their headquarters to connect all offices. This setup ensures efficient communication and easy network growth, letting ABC Corporation stay connected and add new branches smoothly.”
The star topology’s central hub and easy integration make it a top choice for organizations wanting reliability, scalability, and efficient network management.
References:
- Source 1
- Source 2
- Source 3
Bandwidth Requirements
When setting up a WAN network, it’s key to know how much bandwidth you need for good performance. You must look at what your organization does, how many users it has, and what apps and data it uses. This helps figure out the right WAN bandwidth to avoid slow speeds.
Understanding WAN bandwidth needs and how people use the network is crucial. It helps pick the best network setup. It’s important to look at the different types of WAN topologies available to meet these needs well.
In copper cables, twisting wires together helps reduce crosstalk9. This makes the signal stronger and improves how much data can be sent. Also, the type and amount of traffic, and delays from devices, affect how fast data moves9.
Fiber-optic cables are great for long distances and high-speed needs. They don’t get affected by electromagnetic or radio interference, so they can handle more data over longer distances9.
The Physical layer of the network is key for moving data around. It makes sure data is sent smoothly and keeps enough bandwidth for everything9.
UTP cables can face issues like crosstalk and interference from other signals9. Using the right cable management and shielding can help keep the bandwidth good.
In wireless networks, things like cordless phones and microwaves can slow things down9. Good network design and placing devices right can help keep the data moving fast.
Just knowing how much bandwidth you need isn’t enough. You also need to understand how people use the network. By looking at how often and how much data is used, you can make sure there’s enough bandwidth for everyone.
Tools for managing WAN networks give insights into how bandwidth is used. This lets admins see when things get busy and plan for it. This way, the network works well and doesn’t slow down unexpectedly.
Knowing about bandwidth needs and how the network is used helps spot areas to improve. It lets admins make sure important apps get enough bandwidth to work well.
Example Table: Bandwidth Requirements Comparison
| Application | Bandwidth Requirement |
|---|---|
| Low (10 Mbps) | |
| Streaming Video | High (50 Mbps) |
| Voice over IP (VoIP) | Medium (20 Mbps) |
| File Sharing | Medium (20 Mbps) |
Table: Example comparison of bandwidth requirements for different applications
By thinking about WAN bandwidth needs and how the network is used, companies can make a network that works well. This means data moves fast, there’s little delay, and bandwidth is used well. It meets the needs of the company and its users.
Network Topology Considerations
When designing a network, think about WAN network topology, cost, scalability, and redundancy. These factors are key to a network’s success and efficiency.
WAN Network Topology
WAN network topology is about how devices and connections are laid out over a wide area. It includes the setup of routers, switches, and hubs, and how they connect.
There are three main types of networks: Personal Area Network (PAN), Local Area Network (LAN), and WAN10. Knowing the size of your network helps pick the right topology.
Cost and Scalability
Cost is a big deal when picking a network topology. Each type has different costs for setup, upkeep, and growing the network.
Star topologies are cheaper because they need less cabling11. They’re good for small networks on a budget.
Scalability is also key. As businesses grow, their network needs change. A topology that can grow easily is important.
Mesh topologies are very reliable10. But they can be hard to manage and might not be the best for all networks. Think about how your network will grow before choosing a topology.
Redundancy and Reliability
Redundancy is vital for a network’s reliability and uptime. Adding extra parts and connections helps avoid single points of failure.
Star topologies are stable and secure11. If one part fails, the rest keeps working. But losing the central hub takes down the whole network. So, make sure the hub is redundant for reliability.
Ring topologies send data well without errors11. But losing a node can affect the whole network. So, redundancy is key here too.
Other topologies like bus and mesh also have redundancy and reliability issues. It’s important to pick a topology that meets your network’s needs.
Security Considerations
When designing a Wide Area Network (WAN), making sure it’s secure is key. WAN security includes things like encryption, firewalls, and secure ways to access the network from afar.
Using encryption makes WAN traffic safer by protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. It keeps data safe and private, reducing the risk of data breaches. This ensures safe communication between different parts of the network12.
Firewalls are important for keeping the WAN safe by controlling what traffic gets through. With the right setup, firewalls can block harmful activities and stop threats before they get in12.
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) work with firewalls to watch for suspicious network actions. They quickly spot and alert on security issues, helping protect against cyber threats. This helps keep the WAN safe and lowers the chance of cyberattacks12.
Secure ways to access the WAN from anywhere keep authorized users safe. Using VPNs with strong security makes sure data stays safe when sent over public networks. This keeps out unauthorized access and data theft12.
It’s crucial to keep up with the latest security rules and advice when setting up WAN security. Following standards like ISO/IEC 42001 helps make sure the WAN is well-protected1213.
Experts like Miriama Podskubova and Callum Wright are key in making WAN security better. They know a lot about commercial law, IT, and cybersecurity. Their advice helps set up strong security plans and rules1213.
In summary, having strong security is a must for WANs. Using encryption, firewalls, IDS, and secure access keeps data safe and stops unauthorized access. Following standards and getting advice from experts makes sure the WAN is secure1213.
| WAN Security Measures | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Encryption Protocols | Enhanced data integrity and confidentiality |
| Firewalls | Controlled network access and threat prevention |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Proactive monitoring and threat detection |
| Secure Remote Access Mechanisms | Securely connect to the WAN from remote locations |
References
- ISO/IEC 42001 standard provides guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving AI management systems within organizations.
- Miriama Podskubova, an attorney at law, has over a decade of experience specializing in commercial law, focusing on transactions, venture capital investments, IT, digital law, and cybersecurity.
- Callum Wright, Founder and Lead Consultant, has over a decade of experience in cybersecurity, privacy, and AI governance.
- The webinar covers insights into the European Union’s legislative proposal aimed at regulating AI.
Quality of Service (QoS) Prioritization
QoS is key for making networks work better and making sure important apps get the resources they need. It helps manage network traffic well. This means apps that need to work fast get the bandwidth they need, keeping things smooth for things like VoIP or video calls.
QoS uses traffic prioritization to sort and rank different types of network traffic. This makes sure important apps get the bandwidth they need, even when the network is busy. It’s all about making sure critical apps run smoothly.
Traffic shaping is a QoS tool that controls how fast data moves through the network. It sets a limit on how much data can go out at one time. This stops data from getting too slow or causing congestion when it’s more than the network can handle14.
Another tool is traffic policing, which drops packets that go over a certain limit. It’s less effective than shaping but is often used by service providers to stop too much data from coming in. Unlike shaping, it does this before the data even reaches the service provider14.
Traffic policing can also change how packets are marked, like with IP precedence or DSCP values. This lets it manage data packets based on certain rules. It’s used to make sure the network uses its resources well and is often set at the edge of the network14.
For things like video calls, QoS is very important for keeping the quality high. Things like delay, packet loss, and jitter can mess up real-time media over IP networks. By giving priority to packets with media data, QoS can make calls clearer and smoother15.
Using QoS on busy networks can make things better for people using audio and video calls. It makes sure the important media traffic gets priority, reducing the chance of delays or breaks in calls15.
It’s important to remember that Microsoft Teams respects QoS settings within Microsoft’s network but not always on public connections. So, checking the quality of the whole network and the latency of real-time media is a good idea. The quality of the worst part of the network can affect the whole connection15.
In wired networks, QoS can be set up using different queues on a port. Up to 8 queues can be used to treat different types of traffic differently. But, it’s important to know that not all wired networks support things like Approximate Fair Dropping or Discard (AFD)16.
QoS classifies traffic in the IP packet header using bits from the old IP type of service (ToS) field. This lets network devices know how to handle different types of traffic16.
Layer 2 CoS values can also be used for QoS, ranging from 0 for low priority to 7 for high priority. Layer 3 IP packets can carry IP precedence or DSCP values. QoS supports both, making it easy to set priorities for different types of traffic16.
In conclusion, QoS is key for making networks work better and making sure important apps get the resources they need. With tools like traffic shaping and policing, network managers can manage traffic and allocate bandwidth based on priority. This is crucial for real-time media sessions and general traffic, making communication smoother and better for everyone141516.
QoS Tools
| QoS Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Traffic Shaping | Regulates and smooths out packet flow by applying a maximum traffic rate for each interface’s egress queue |
| Traffic Policing | Drops packets that exceed specified limits rather than queuing them |
| QoS Prioritization Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Latency | Affects the real-time nature of audio and video communications |
| Packet Loss | Can result in audio and video distortions or dropouts |
| Jitter | Can cause variations in audio and video quality over IP networks |
Conclusion
Optimizing WAN design is key for businesses to meet their network needs. It’s about looking at bandwidth, network setup, security, and making sure certain services get priority. This way, companies can have a strong and efficient WAN that supports their work.
Mesh topology is the top choice for many because it makes networks more efficient and reliable17. It’s great for smart homes and sensor networks. For data centers and super-fast computing, wired mesh networks are the go-to.
When setting up QoS, it’s important to get traffic priority right. Audio calls get top priority at 55%, followed by financial dealings at 35%, and web pages at 10%18. Cloud computing is a big win for networking, letting companies grow their networks without spending on new gear, with a 75% boost18.
For a secure and efficient WAN, network teams need to get the basics of WAN design. They should know how mesh networks work with their nodes and links17. With a solid grasp of these ideas, businesses can aim for the best network performance that fits their specific needs and hurdles.
FAQ
What is WAN topology?
WAN topology shows how a wide area network connects different places. It tells us how devices are linked and how data moves between them.
What are the different types of WAN topologies?
WAN topologies include point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, full mesh, ring, and star. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks.
What is point-to-point topology?
Point-to-point lets two places exchange Ethernet frames directly. It uses dedicated lines or Metro Ethernet (MetroE).
What is point-to-multipoint topology?
In point-to-multipoint, a central site sends data to many places. But, those places can only send data back to the center.
What is full mesh topology?
Full mesh lets all devices talk directly to each other. It’s often used for Ethernet LAN services.
What is ring topology?
Ring topology connects devices in a loop. It can reroute traffic if there’s a problem. Adding new sites can be tricky and expensive.
What is star topology?
Star topology uses a central hub. It makes adding new parts easy. Each device connects directly to the hub, making it less likely to fail completely.
How do I determine the required WAN bandwidth?
To figure out WAN bandwidth needs, look at your organization’s size, apps, and data moving around. This helps avoid network slowdowns.
What factors should I consider when selecting a network topology?
Think about cost, how big it can grow, and how reliable it is. You can choose from point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, or full mesh topologies.
How can I ensure security in WAN design?
Use strong security like encryption, firewalls, and secure access. This keeps data safe and stops unauthorized entry.
Why is quality of service (QoS) prioritization important in WAN design?
QoS makes sure important apps get the resources they need. This cuts down on delays and keeps things running smoothly for urgent tasks like VoIP or video calls.
What factors should be considered for WAN optimization?
For WAN optimization, think about bandwidth, network design, security, and QoS. Knowing these helps build a strong, efficient WAN that fits your organization’s needs.
Source Links
- https://network-insight.net/2014/12/08/wan-design-considerations/ – Wan Design Considerations
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-physical-and-logical-topology/ – Difference between Physical and Logical Topology – GeeksforGeeks
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/sdwan/configuration/routing/ios-xe-17/routing-book-xe/m-unicast-routing.html – Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.x – Unicast Overlay Routing [Cisco SD-WAN]
- https://www.manageengine.com/network-monitoring/tech-topics/network-topology.html – Network Monitoring Software by ManageEngine OpManager
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/SDWAN/cisco-sdwan-design-guide.html – Design Zone for Branch/WAN – Cisco SD-WAN Design Guide
- https://www.guru99.com/type-of-network-topology.html – Types of Network Topology: Bus, Ring, Star, Mesh, Tree Diagram
- https://www.numerade.com/ask/question/a-network-team-is-comparing-physical-wan-topologies-for-connecting-remote-sites-to-a-headquarters-building-which-topology-provides-high-availability-and-connects-some-but-not-all-remote-site-43599/ – A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/tip/6-types-of-enterprise-networking-topologies – 6 types of network topologies | TechTarget
- https://www.brainscape.com/flashcards/modul-4-7-13798249/packs/21502316 – Modul 4-7 Flashcards by Jona CCNA
- https://www.vaia.com/en-us/explanations/computer-science/computer-network/types-of-network/ – Types of Network: Topology, Computer Models
- https://www.dnsstuff.com/what-is-network-topology – What is Network Topology? Best Guide to Types & Diagrams – DNSstuff
- https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/ccnav5org-ccna-1v50itnpracticefinalexamanswers/36518746 – Ccnav5.org ccna 1-v50_itn_practice_final_exam_answers
- https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/ccnav5org-ccna-1v50itnpracticefinalexamanswers-36519537/36519537 – ccna 1 v5.0 itn practice final exam answers
- https://study-ccna.com/qos-traffic-shaping-policing/ – Quality of Service (QoS) Traffic Shaping and Policing – Study CCNA
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/skypeforbusiness/optimizing-your-network/media-quality-and-network-connectivity-performance – Media Quality and Network Connectivity Performance – Skype for Business Online
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst9500/software/release/16-9/configuration_guide/qos/b_169_qos_9500_cg/configuring_qos.html – Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.9.x (Catalyst 9500 Switches) – Configuring QoS [Support]
- https://www.wevolver.com/article/mesh-topology – Mesh Topology: A Deep Dive into Principles and Applications
- https://github.com/ferib/CCNA-Exam-Answers-2019—DUMP/blob/master/CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2019 (v5.1+v6.0) Introduction to Networks.txt – CCNA-Exam-Answers-2019—DUMP/CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2019 (v5.1+v6.0) Introduction to Networks.txt at master · ferib/CCNA-Exam-Answers-2019—DUMP