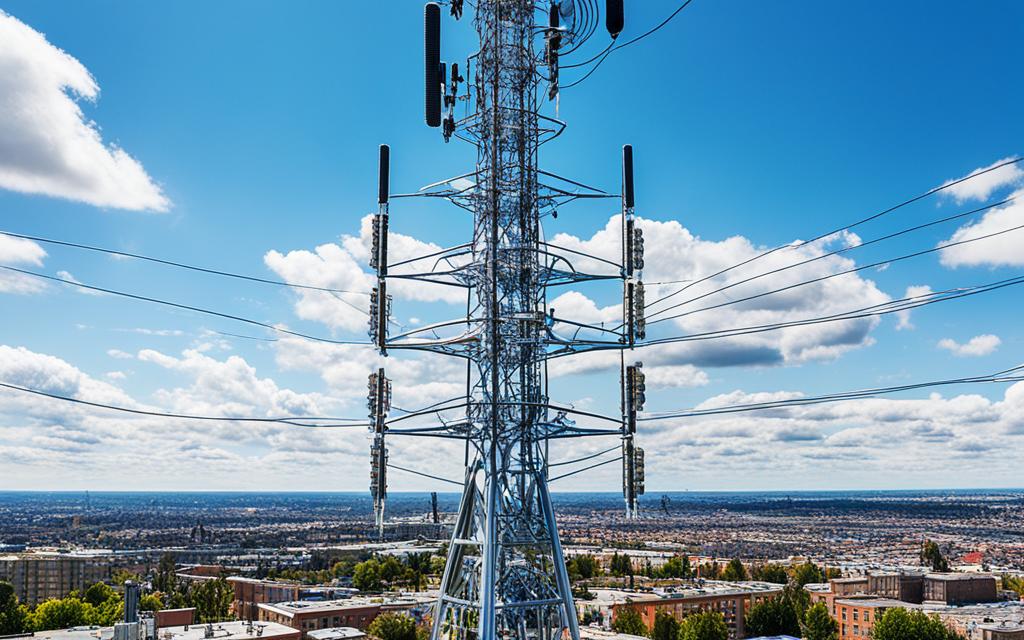
Cell towers are key for sending calls over long distances in a cellular phone network. They have antennas and radio gear that let phones connect. There are many types, like panel and sector antennas, each designed for better coverage and capacity1.
Cell towers do more than just send signals. They receive calls from phones and send them to a switching center. This center connects the call to another phone or network, making calls possible locally and worldwide2. Inside each tower, a Base Transceiver Station (BTS) handles calls and does important tasks like signal processing and encryption1.
How far cell towers can reach depends on many things. In the countryside, they can go up to 20 miles. But in cities, it’s usually just a mile or two because of things like signal strength and tall buildings1. New tech like MIMO and beamforming helps them reach farther and improve signal quality1.
Cell towers are crucial for good wireless communication. They need a clear line of sight for strong signals, especially for 5G technology1. Phones work like radios, sending and getting signals to and from cell towers. Signals sent by phones are called uplinks, and those sent by towers are downlinks2.
Key Takeaways:
- Cell towers are vital for sending calls and keeping communication smooth in cellular networks.
- Antennas on towers catch signals from phones, connecting them to the network.
- The BTS in a tower supports many calls at once and does important tasks like signal processing.
- How far cell towers can reach depends on things like signal strength and tall buildings.
- Modern towers use tech like MIMO and beamforming for better range and signal quality.
Cell towers make high-speed internet possible for things like browsing and streaming videos. They’re also key in emergencies for communication and rescue efforts. They work with GPS for accurate navigation and support IoT devices in smart homes and cars3.
Cell towers affect property values based on their location and how they look. They need regular upkeep for constant network coverage, including backup batteries during power cuts. Putting up a cell tower can be a way for property owners to earn extra money3.
What Is a Cell Tower and How Does It Work?
A cell tower, also known as a cell site, is a structure that houses electric communications equipment and antennas. It helps phones and radios work in the area. When you use your cell phone, it sends out a signal that the nearest cell tower picks up.
The tower then sends the signal to a switching center. This center connects the call to another phone or a network. Cell towers let devices connect and send data, so you can call, text, browse the internet, and use wireless services.
Over 165,000 cell towers and 375,000 cell sites4 handle thousands of connections at once. These towers are placed to give the best coverage and keep communication smooth over a wide area.
There are four main types of cell phone towers:
- Monopole towers4 are 50 to 200 feet tall and fit well in cities. They are slim and don’t stand out much.
- Lattice towers4 are 200 to 400 feet tall, sometimes reaching 1,000 feet. They’re used in places that need more coverage.
- Guyed towers4 use support wires and can be 200 to 2,000 feet tall. They’re good for areas with strong winds because they’re stable.
- Stealth towers4 look like trees or flagpoles. They’re used in places where looks matter a lot or where rules are strict.
Cell towers can be anywhere from 50 to 400 feet tall5. Their design and height depend on local rules, coverage needs, and the area’s geography.
Cell towers are key for wireless communication. They make sure signals go from devices to the network over long distances. They’re the main part of the cellular network, handling data and voice signals.
A cell tower’s signal can reach up to 25 miles, sometimes 45 miles4. But its coverage area is usually small, about 1 to 3 miles outside cities and 0.25 to 1 mile in cities4.
Cell towers are vital for a strong signal and reliable wireless services. They keep people and businesses connected, letting them access information and communicate easily in our connected world.
As technology gets better and we use wireless more, cell towers are crucial for the cellular networks. Next, we’ll look at the different cell towers and what they do in the wireless world.
Types of Cell Towers and Their Components
Cell towers are key to wireless communication networks. They come in different types, each with its own parts. These parts work together to keep our phones connected. Let’s look at the main types of cell towers and what makes them work.
Types of Cell Towers
There are four main types of cell towers: monopole, lattice, guyed, and stealth towers.
- Monopole Towers: These are tall, slim poles that fit well in cities and suburbs.
- Lattice Towers: These have a framework with open steel legs. They’re often found in rural areas and high places.
- Guyed Towers: These are tall masts held up by wires. They’re used where height is needed and space is tight.
- Stealth Towers: These towers look like trees or other natural things. They’re chosen by communities that want to keep things green.
Each type of cell tower meets different needs, making sure we stay connected everywhere.
Cell Tower Components
Cell towers have parts that work together to keep us connected. These parts include:
- Antennas: These send and receive signals. Each tower can have many antennas to improve communication.
- Transceivers: These have the radio gear for sending and getting signals between towers and phones.
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS): The BTS has the transceivers, power boosters, and other gear for sending signals.
- Towers or Masts: These give the height needed for wide coverage, so signals can reach far.
- Ground-Based Equipment: This includes boxes or shelters for extra systems like power sources, backup power, and cooling.
- Microwave Dishes: These dishes connect cell towers to each other, helping in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
- Cabling: Cables and fiber lines link the cell tower parts together, making sure signals move smoothly.
- Utility Installations: Towers need heating or cooling units, backup power, and safety gear to work well.
Antennas are key for cell towers. They send and receive signals for clear communication.
Building cell towers means following FCC rules, thinking about the environment, telling the FAA, registering antennas, and following local zoning laws6. Putting all these parts together makes sure our wireless networks work well and we can communicate easily.
How Cell Towers Function in Wireless Communication
Cell towers are key to wireless communication. They make sure mobile networks work well. They send and receive signals to and from mobile devices. This keeps voice calls, messages, and data transfer reliable.
Cell towers have antennas, transceivers, and a base station. Antennas pick up signals from devices and send them to the base station. Transceivers change signals into a format that can be sent over the network. The base station controls how calls and data move through the network.
Antennas on cell towers are placed to give the best coverage. They work on different frequencies for voice and data. The distance a cell tower can reach depends on the terrain, power, frequency, height, and design. Typically, a cell tower can reach up to 45 miles7.
In places with lots of cell traffic, like cities or big events, towers can get too busy. To fix this, repeaters and hybrid DAS systems can boost signals up to 32 times7. Solutions like WilsonPro help improve signal strength and quality in crowded areas.
Some millimeter wave frequencies don’t go far, only about 300 to 500 feet7. To fix this, many small cell towers are set up close together. This gives continuous coverage and more capacity.
WilsonPro repeaters and DAS solutions don’t need carrier approval or big system changes7. This makes them a smart and affordable way to boost cell signal.
Cell towers are vital for wireless communication. They work with other network parts to keep connections smooth. Understanding how they work shows us their importance in today’s communication.
Want to learn more about cellular networks and cell towers? Check out these resources:
Cell Tower Range and Factors Affecting Coverage
The range of a cell tower varies by several factors. In rural areas, towers can reach up to 25 miles. In cities, it’s usually 1 to 3 miles8.
Many things affect how far a cell tower’s signal goes. The terrain, like mountains and hills, is a big factor. So are buildings. The frequency band used also matters. Signals on lower frequencies can go further, up to 25 miles, while higher frequencies cover much less ground8.
The antenna’s height is key too. Taller antennas can reach over hills and valleys. In flat areas, signals can stretch up to 45 miles. But in mountains, the range is much shorter8.
The power of the signal is another big factor. It affects how far and strong the signal is8.
Cell towers don’t just work alone. They work together to cover a wide area. In busy places, towers are closer together because signals don’t go as far8.
Cell towers don’t work alone. They form a network for better coverage. But things like buildings and hills can block signals. Also, too many devices on the same frequency and network crowding can make signals weak9. So, picking a network with strong signals is important9.
In summary, many things affect how far a cell tower’s signal goes. Knowing these helps both network providers and users improve signal quality89.
Safety Standards for Cell Towers
Cell towers are key to our phone network, keeping us connected. They follow safety standards to protect us. These standards cover RF energy limits and how antennas work.
Cellular or PCS cell site towers are typically 50-200 feet high10. The FCC sets rules for these towers. They allow up to 500 watts per channel, based on the tower’s height10. Most towers in cities use 100 watts or less10. This means they emit only 5-10 watts in cities10. In cities, towers usually send out 10 watts or less per channel10.
There’s a limit on how much RF energy we can be exposed to. It’s about 580 microwatts per square centimeter10. But, this can be a problem for people working near antennas. They can take steps to avoid too much exposure10.
There are also worries about the health effects of RF radiation from cell towers. But, lots of research shows that the RF energy from towers is safe11. The levels of exposure are much lower than safety limits11. Inside buildings, the exposure is even lower because of building materials11.
The American Cancer Society hasn’t taken a stand on cell towers and cancer11. The IARC says RF radiation might increase the risk of some brain tumors11. But, the FDA says there’s no clear link between RF radiation and tumors11. Most studies haven’t found a link between living near cell towers and cancer11.
Overall, cell towers follow safety standards to limit RF energy and protect us1011. These rules and research help us use our phones safely1011. By following these standards, we can use our phones without worrying about risks to our health.
Evolution to 5G and Its Impact on Cell Towers
The move from 4G to 5G has changed the game in speed, capacity, and latency. It’s a big deal for the telecom world.
5G can hit speeds of up to 20 Gbps, a huge jump from 4G’s 1 Gbps. This means faster streaming, quicker downloads, and smoother online actions12.
5G also cuts down on wait time, with speeds as fast as 1-2 milliseconds. This makes for real-time chats and opens doors to new tech like IoT and AI12.
New radio bands in 5G mean super-fast speeds. This is key for handling data quickly, making it perfect for IoT and AI12.
5G is way better than 4G in speed, capacity, and latency. It’s a huge step forward in wireless tech12.
Edge computing is now a thing, thanks to 5G. It processes data close to where it’s made to cut down on wait times. This makes 5G even faster and more efficient12.
5G came about thanks to work from companies, schools, and tech groups worldwide. Big names like Ericsson and Samsung helped make 5G a reality, starting a new chapter in connectivity12.
5G isn’t just about networks; it’s also changing cell towers. Modern towers can handle thousands of calls or connections at once, keeping up with more devices1.
To improve coverage and reduce signal mix-ups, cell towers use sector and panel antennas. These technologies boost capacity and signal strength1.
In 5G, high-frequency signals go shorter distances but carry more data. Lower frequencies in rural areas go farther but carry less data. Tower height is key for coverage, with taller towers reaching farther and getting past obstacles1.
Cell towers use microwave dishes for communication in remote spots without cables. This is vital for reaching areas hard to connect otherwise1.
Cables like coaxial and fiber optic link cell tower parts for smooth communication. They’re crucial for data and signal transfer, keeping the network running well1.
As 5G grows, cell towers are crucial for meeting its high demands. They’re getting better and ready for a more connected future.
Cells-On-Wheels and Temporary Cell Service
When power goes out or equipment gets damaged, keeping cell service going is key. That’s where cells-on-wheels (COWs) step in. These are mobile units that quickly set up to give temporary cell service. They make sure people can keep in touch until things get back to normal13.
COWs are set up in places where cell service is really needed, like at big events or after disasters13. They can be put together and taken down fast, helping with urgent communication needs13.
COWs help ease network congestion, making sure there’s enough space for calls and data13. They support many wireless technologies, like 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G, depending on what the network needs13. This makes them key for events and emergencies, helping to keep people connected13.
COWs are also used in places hard to reach or where putting up permanent towers is tough13. They’re a big help in natural disasters, quickly getting communication services back online13.
Tower Solutions is a leader in portable cell towers. Their towers can hold over 2000 lbs, making them useful for many industries14. What makes them stand out is how easy they are to set up. One person can get them ready in just 5-15 minutes, which is a big time saver14.
These towers can be raised to heights of up to 120 feet, giving better coverage and connections14.
At Super Bowl LII in 2018, Tower Solutions’ towers were used to boost broadband and cell service. This showed how versatile they are for big events14. These towers have been tested by the U.S. military in dangerous areas and have proven to be strong, quick to set up, and lifesaving in emergencies14.
To find out more about cells-on-wheels and how they work, check out these resources:
- LinkedIn – Cells on Wheels (COWs)
- Millman Land – What Is a Cell Tower and How Does It Work
- Tower Solutions – Portable Cell Towers and Cells-On-Wheels
Conclusion
Cell towers are key to our wireless communication, covering vast areas. They connect calls and data between devices and the network. Over time, they’ve changed from big stations to smaller ones, making networks better and bigger15.
Safety rules protect us from harmful radio waves from cell towers and devices. Studies show that these waves don’t pose a big health risk. They mainly cause heating and nerve effects, staying below safe levels16. Also, there’s no link between 5G and COVID-19 or cancer16.
5G technology is making cell towers even better at connecting us. It uses smaller towers and antennas to cover shorter distances. This setup gives us a strong signal everywhere17.
In summary, cell towers are changing how we communicate, offering wide coverage and safety. They’re key to the digital changes we see, connecting us all151617.
FAQ
What is a cell tower and how does it work?
A cell tower, also known as a cell site, is a structure that houses electric communications equipment and antennas. It helps with wireless communication for phones and radios in the area. When you use your cell phone, it sends out a radio wave that the nearest cell tower receives.
The tower then sends the signal to a switching center. This center connects your call to another phone or a network.
What are the types of cell towers and their components?
There are four main types of cell towers: monopole, lattice, guyed, and stealth towers. These towers have important parts like antennas, transceivers, and base transceiver stations (BTS). They also have towers or masts, ground-based equipment, microwave dishes for backhaul, cabling, and utility installations.
How do cell towers function in wireless communication?
Cell towers work by getting signals from mobile devices with antennas and turning them into digital signals. These signals then go to the network through backhaul connections. The base station manages communication protocols and sets up, maintains, and ends calls or data sessions.
The tower’s antennas send and receive signals. This provides coverage and capacity for thousands of voice and data connections.
What factors affect cell tower range and coverage?
The range of a cell tower depends on things like the terrain, transmitter power, frequency band, antenna height, and antenna type. Higher antennas can cover more area by overcoming obstacles.
What are the safety standards for cell towers?
Cell towers follow safety standards set by groups like the FCC. These standards limit how much RF energy cell antennas can send out to protect health. Towers often have fences and signs to keep people away from the antennas.
How does the evolution to 5G impact cell towers?
5G technology improves speed, capacity, and latency over 4G. Cell towers are key to better network performance and capacity. Research and safety standards make sure cell towers and wireless networks are safe for public health.
What are cells-on-wheels and their role in temporary cell service?
COWs, or cells-on-wheels, are portable structures for temporary cell service. They are used during power outages or equipment damage to keep cell service going. COWs are vital for keeping connectivity during emergencies and ensuring service in tough situations.
Do cell towers affect public health?
There are concerns about the health effects of RF radiation from cell towers. But, lots of research and rules make sure the RF energy is safe. Ongoing research and safety standards protect public health.
Why are cell towers important in cellular phone networks?
Cell towers are key for cellular phone networks, making sure wireless communication works well. They send and receive signals from devices, connecting calls and data to the network. Cell towers also improve network performance, capacity, and coverage range. Safety standards and rules limit the RF energy emitted by cell towers. Cell towers are crucial for modern communication networks, giving us the connectivity we need every day.
Source Links
- https://www.ni.com/en/solutions/semiconductor/wireless-infrastructure-development/how-cell-towers-work.html – How Cell Towers Work to Keep You Connected
- https://toweradvantage.com/how-does-a-cell-tower-actually-work/ – How do Cell Towers Work? | Tower Advantage, Cell Tower Lease Experts
- https://www.cellnex.com/gb-en/news/cell-towers-how-they-work-and-why-they-matter/ – What Is A Cell Tower? | How They Work And Why They Matter | Cellnex UK
- https://dgtlinfra.com/what-is-a-cell-tower-how-work/ – What is a Cell Tower? Understanding How Cell Towers Work
- https://www.wilsonamplifiers.com/blog/cell-towers-everything-you-ever-wanted-to-know/ – What are Cell Towers and How Do They Work?
- https://btussel.com/education/everything-you-need-to-know-about-cell-towers/ – Everything You Need to Know About Cell Towers | Bug Tussel
- https://www.wilsonpro.com/blog/how-are-cellular-networks-built – How Are Cellular Networks Built? | Blog
- https://dgtlinfra.com/cell-tower-range-how-far-reach/ – Cell Tower Range: How Far Do They Reach?
- https://www.ask.com/news/understanding-factors-affecting-mobile-phone-signal-quality-location – Understanding the Factors Affecting Mobile Phone Signal Quality in Your Location
- https://www.fcc.gov/consumers/guides/human-exposure-radio-frequency-fields-guidelines-cellular-and-pcs-sites – Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Fields: Guidelines for Cellular Antenna Sites
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/radiation-exposure/cellular-phone-towers.html – Do Cell Phone Towers Cause Cancer?
- https://www.tdk.com/en/tech-mag/past-present-future-tech/what-is-5g-and-why-is-it-important – 5G: Understanding the Technology that’s Changing Connectivity
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/cells-wheels-cows-miguel-macia – “Cells on Wheels” (COWs)
- https://towersolutionsinc.com/application/portable-cell-towers-cell-on-wheels-cows/ – Portable Cell Towers | Cell On Wheels (COWs) | Tower Solutions
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/cellular-telephone – Cellular Telephone – an overview
- https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/health-risks-safety/radiation/everyday-things-emit-radiation/cell-phones-towers.html – 5G technology, cell phones, cell phone towers and antennas
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-cell-towers-work-backbone-your-mobile-amr-elharony-sspjf – How Cell Towers Work: The Backbone of Your Mobile Connectivity 📱🗼