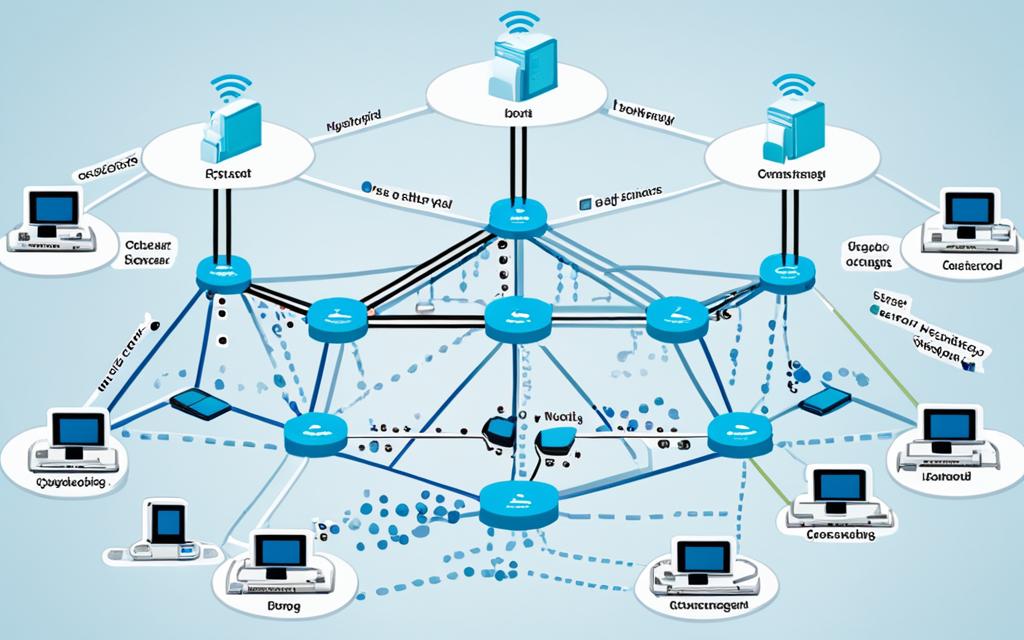
Network topology is about how devices and connections are set up in a computer network. It shows how these parts work together. Knowing about different network topologies helps make networks work better and last longer. There are many types, like bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree, each with its own good and bad points.
Choosing the right network topology can make a big difference in how well a network works. It can make it use less energy and send data faster1. There are many kinds of network topologies, such as Bus, Star, Ring, Mesh, Tree, and Hybrid, each with its own special features and uses12. Logical topologies show how data moves in a network and connect devices in a certain way1. Network diagrams are key for network managers to fix problems, use resources well, and solve network issues1. Many tools, like Datadog and Edraw, help make detailed diagrams of network topologies1. Tools for managing and checking network performance also help network admins with complex networks1.
Key Takeaways
- Network topology is about how elements are arranged in a computer network12.
- Common types of network topology include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree2.
- The choice of network topology affects performance, energy use, and how fast data moves1.
- Network topology diagrams are key for fixing problems and managing resources1.
- There are many tools to make detailed diagrams of network topologies1.
Knowing about network topology is key for keeping networks running well, solving problems, and saving money in different fields2. Planning your network right can cut energy use, speed up data transfer, and make the network more efficient2. Network topologies are crucial for understanding how networks work, cutting costs, and finding problems and fixing them2. They offer ways to manage risks, respond to attacks, and recover quickly based on what’s best for your needs2. When designing a network, it’s important to think about different topologies to balance benefits and risks2.
Types of Network Topology
There are many types of network topologies, each with its own benefits and challenges. Knowing about these can help organizations pick the best setup for their needs. Let’s look at some common network topologies and their features.
Point-to-Point Topology
Point-to-point topology is the simplest network setup [source]. It connects two devices directly, allowing them to talk to each other. This type is cost-effective and has less delay than other networks3. You’ll find it in things like phone lines and leased lines.
Mesh Topology
In mesh networks, every device connects to every other, making a fully connected network [source]. This makes the network very resilient, as data can switch paths if a link fails4. But, it needs a lot of cables, especially in wired setups5. To figure out how many ports you need, use the formula N * (N-1), where N is the number of devices5.
Star Topology
The star network is a common setup in today’s networks [source]. All devices link to a central hub or switch. This hub is where all communication goes through, making it easier to fix problems and keep the network secure3. Adding devices to a star network is simple, needing only one cable for each device5.
Bus Topology
Bus topology uses one channel for all devices to connect to [source]. It’s affordable and easy to grow by adding more devices. But, it’s not often used in big networks because it can get slow4. Sending data to all devices at once can slow things down4.
Ring Topology
Ring networks have devices in a circle, with data moving from one to another until it reaches its destination [source]. This setup is fast and cuts down on data mix-ups, making it good for certain tasks5. But, fixing problems in a ring network can be hard, as one broken link can stop the whole thing5.
Tree Topology
Tree topology, or hierarchical topology, has a structured network with layers . It’s becoming more popular in data centers. This design makes adding new devices easy and helps find and fix errors quickly5.
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology mixes different network types for better performance, reliability, and cost . It’s common in business networks, often using a star setup for most connections. In some cases, a wireless mesh network is added for better connectivity. This approach lets you design complex networks flexibly.
Knowing about network topologies is key for building efficient and reliable networks. Each type has its own pros and cons, so picking the right one is important for the network’s size and goals3. By thinking about cost, how easy it is to add devices, how fast data moves, and how resilient the network is, businesses can make their networks better and keep everyone connected smoothly.
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Point-to-Point | Simple, cost-effective, low delay in communication | Limited scalability, direct connection required |
| Mesh | High network resiliency, robust communication | Complex cabling, higher cost |
| Star | Easy troubleshooting, enhanced network security | Dependency on central hub, single point of failure |
| Bus | Cost-effective, simple network structure | Potential network congestion, reduced performance |
| Ring | High-speed data transmission, reduced collisions | Troubleshooting challenges, single failure impact |
| Tree | Scalable, error detection and correction | Complex configuration, potential bottlenecks |
Choosing the right network topology needs careful thought about what an organization needs and wants. By looking at factors like cost, how easy it is to add devices, troubleshooting ease, and security, businesses can create a strong and efficient network. This supports their operations and boosts overall connectivity and productivity.
Point-to-Point Topology
Point-to-point topology is key in network structures, making sure communication between two nodes is efficient. It creates a direct link between the sender and receiver. This ensures a reliable and dedicated connection6.
This type of topology is used in many fields like telecommunications and satellite communications. It’s vital when direct communication between two nodes is needed. It offers reserved bandwidth, leading to high-speed data transfer with low latency. Its simple design makes it an efficient choice for direct connections6.
Unlike point-to-point, other topologies like bus, ring, star, tree, and mesh use more nodes or central hubs for data. These topologies are made to meet specific needs and challenges of organizations67.
Let’s look at some common network topologies and what makes them unique:
Bus Topology
In bus topology, all nodes connect to one cable, forming a line. This cable is the main way data moves, with terminators at each end to stop data from bouncing back. It’s easy to set up but can fail if the main cable is damaged6.
Ring Topology
Ring topology is a loop where data moves from one node to the next, either one way or both. Each node helps send data through the network. It’s strong against cable failures but can be hard to change the number of nodes6.
Star Topology
Star topology has a central hub that connects all nodes. This hub helps send and manage data, making it easy to add more nodes and fix problems. But, it can fail if the central hub goes down6.
Tree Topology
Tree topology looks like a branching structure, great for big networks. It’s good for growing networks and is often used in complex setups. But, relying on the root node can cause problems if not managed well6.
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology connects all nodes, allowing data to move through many paths. Each node helps send data, making sure it reaches its destination. This makes it very reliable and able to reroute data if needed. Mesh is used where keeping communication going without breaks is key68.
Each network type has its own pros and cons in setup, upkeep, and performance. Companies need to think about their needs and pick the best topology for their communication goals678.
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, every device connects to another via dedicated channels. This creates a network where every node talks directly to every other. It’s great for places needing fast communication between nodes. The focus on dedicated links boosts the network’s speed.
Mesh topologies enhance redundancy and fault tolerance by offering many paths for data. If one link or device goes down, data can switch to another path. This keeps communication going. Mesh topologies are key in military, aircraft, and internet systems9.
Mesh topologies come in two types: full mesh and partial mesh. Full mesh means every device connects to every other, offering lots of redundancy. But, it needs a lot of connections, making it best for small networks. Partial mesh connects some devices directly, balancing cost with communication needs9.
Wireless networks like wireless sensor networks and wireless mesh networks often use mesh topologies. They use mesh’s flexibility to send data efficiently and reliably. Protocols like AODV and OLSR help manage data in mesh networks, making them work better9.
But, managing big mesh networks is tough. You need to optimize routes, manage devices, and watch the network closely. Mesh networks deal with congestion by changing routes and controlling data flow. This keeps data moving smoothly, even when it’s busy9.
Hybrid networks mix mesh and star topologies for more flexibility. They offer good communication, fault tolerance, and are easier to manage and grow9.
To keep wireless mesh networks safe, use encryption and control who can get in9. Mesh topology has many perks, but designing networks well is key. Think about what you need and design with care to make the most of mesh topology9.
Star Topology
In a star topology, all devices link to a central hub with their own cables. This hub is like a server, managing the network. They are simple to set up and manage, perfect for needs that value easy setup and management10. Adding or removing nodes is easy, making them flexible for growth or changes11. Star topologies are often seen in local area networks (LANs) and wireless setups. They are reliable, making them great for industries like automotive or robotics11.
The star setup has a central hub, which can be a Switch or a hub. A switch boosts routing and regeneration, making it the top choice for star networks10. This hub makes managing the network simple, as each device connects directly to it. If one device fails, it won’t mess with others, thanks to this design10.
Star topologies are used in many places, from schools to homes and even in banking10. They connect devices like computers, laptops, printers, and servers. Adding new devices is easy, without harming the network’s speed or function10.
But, star topologies have their downsides. More devices can slow down the network and reduce speeds10. The network’s layout also matters. If devices are far apart, using the right cables and fast connections is key for good performance12.
Bus Topology
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable, forming a linear network.
This single cable is known as the “bus” and serves as the communication medium for all connected devices.
Bus topologies are highly cost-effective due to their use of a single cable. They are suitable for smaller LAN setups and environments where budget constraints are a concern. This cost-effectiveness comes from needing less cable length compared to other network architectures13. Also, the design of bus topology is straightforward, making it easy to understand and implement13.
While being inexpensive to set up, bus topologies have limitations. Adding more devices can degrade signal quality due to signal bouncing and reflections. The bus’s limited length also affects network scalability, making it best for smaller networks13.
Cable failures, signal degradation, and collisions are common issues with bus topology. But, these can be fixed with proper network design and cable management. Coaxial cable and twisted-pair cable are often used in bus topology networks, offering reliable and stable connections14.
Bus topology isn’t right for every situation. It’s often used in small to medium-sized LANs, industrial control systems, building automation systems, and small office/home office (SOHO) networks14. It’s also used in legacy systems that haven’t moved to modern networks because it works with older hardware and software13.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Cost-effective due to using a single cable13 | Signal degradation as more devices are added13 |
| Easy to set up and understand13 | Restricted network scalability13 |
| Compatible with older hardware and software13 | Potential cable failures, signal degradation, and collisions14 |
Ring Topology
In a ring topology, devices are linked in a circle, making a closed loop. Data moves in one direction. This setup gives everyone equal access to network resources and keeps devices in a circle. Token Ring and Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) use this network type.
Ring topology’s main plus is its one-way data flow. This cuts down on data mix-ups and boosts network speed. Data moves from one device to the next, avoiding data clashes. It’s great for apps needing one-way data flow.
Yet, ring topology isn’t as common today as Ethernet. Networks often switch to star or mesh for better performance or support. But, ring topology’s past importance might bring it back with new tech and changing network needs.
A big minus is that a single broken link can take down the whole network. This makes it a single weak spot. Finding network problems in a ring can also be tough because of its circular setup.
Setting up a ring network needs special hardware, like Token Ring adapters, which costs more than Ethernet gear. The cabling for a ring setup can be complex and slow, affecting network growth and speed.
Using two rings together can make a network more reliable. This setup means data can keep moving even if one ring stops working.
Ring topology isn’t as popular now, but it’s still used in some places. It’s seen in industrial control systems and some old LANs/WANs. Its unique benefits and history make it still useful in certain situations.
Key Points:
- Devices in ring topology are connected in a circular network, forming a closed loop.
- Data flows in a unidirectional manner in ring topology, reducing packet collisions.
- Ring topology emphasizes equal access to network resources and arranges devices in a circular pattern.
- Token Ring and FDDI are examples of network technologies that use a ring topology.
- Advantages of ring topology include efficient data transmission, prevention of collisions, and high performance.
- Disadvantages of ring topology include the risk of network failure if a connection or workstation is broken, troubleshooting complexity, and higher hardware costs.
- Dual-ring configurations provide fault tolerance and redundancy in ring topology.
- Ring topology may still be used in specialized applications and has historical significance in networking.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Efficient data transmission | Network failure if a connection or workstation is broken |
| Prevention of collisions | Troubleshooting complexity |
| High performance | Higher hardware costs |
| Equal time share access |
15 References:
– https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/r/ringtopo.htm
– https://www.cbtnuggets.com/blog/technology/networking/why-still-use-a-ring-network-topology
– https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/what-is-ring-topology/
Tree Topology
Tree topology is a network setup that combines bus and star topologies. It’s one of the five main network types16. This setup looks like a tree, with a main node and many branches16. It’s great for big companies with many departments, helping organize and segment networks17. Tree topologies grow easily by adding more star networks to the main cable16. This helps big companies handle network growth17. Plus, nodes can connect to several hubs, offering backup paths if something fails17.
Tree topology is often used in small LANs16. It boosts security, especially with smart hubs, making error spotting easy16. Troubleshooting is simpler because problems can be found in one branch without affecting the whole network17. Switches and routers manage data traffic, cutting down on delays and ensuring messages get to their destinations17. But, consider latency and speed when talking across long distances17.
In CAN bus networks, tree topology is one of the main types, along with linear, star, and ring18. Linear bus is good for small to medium networks, being affordable and easy to maintain18. Star bus connects all nodes to a central hub, great for large networks to reduce delays18. Tree bus combines linear and star, letting many sub-networks connect through hubs for complex setups18.
For a working CAN bus network, you need a CAN controller chip, physical layer converter, proper power, and the right connectors and cables18. Managing a CAN bus network means handling node placement, speed, finding faults, security, and improving performance18. To fix issues with long CAN buses, shorten branches, add resistors, or use CAN relay or hub devices18.
Advantages of Tree Topology
- Provides a hierarchical flow of data
- Easy scalability for network growth
- Enhanced security with error identification at individual nodes
- Efficient network troubleshooting
With these benefits, tree topology is a top choice for organizations needing a scalable, hierarchical network setup.
Hybrid Topology
A hybrid topology mixes two or more topologies for flexibility. It lets networks be customized to fit specific needs. This mix of topologies, like ring, bus, and mesh, creates a strong system. It’s efficient and reliable, perfect for complex networks.
Hybrid networks are reliable because they quickly find and fix errors and can handle faults well19. They work efficiently by fixing the weaknesses of each topology, making sure data moves well19. These networks can be changed to meet the needs of users and organizations, offering a tailored solution19. They also grow easily, adding or removing parts without affecting the network19.
Hybrid topologies are more secure19. They keep the whole network safe from threats and errors, making data safer19. But, they can be hard to set up and need network experts19. Putting together a hybrid network is tough because of the complex setup and the need for more hardware and cables19. Keep these points in mind when planning and setting up a hybrid topology.
Hybrid topology is popular in fields like telecommunications, IT, and big businesses20. It’s great for handling lots of data, ensuring reliable connections, good performance, and high security2021. It’s also easier to find and fix problems in hybrid topologies than in others like ring or tree21. Handling a lot of traffic is another big plus, making it good for big areas21.
In summary, hybrid topology combines the best of several topologies for a flexible, scalable, and secure network. It might need more expertise and resources to set up, but its reliability, efficiency, and customization make it a top choice for complex networks.
Conclusion
Network topology is key to making networks work well and reliably for companies. Knowing about the different network topologies helps network managers make smart choices. This ensures their networks meet their needs.
There are several network topologies like bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid22. Bus topology is great for small networks because it’s easy to set up and doesn’t cost much. It’s perfect for fast data transfer, but it can’t handle big networks because of the cable length22.
Star topology is easy to install and reliable, making it great for big offices and campuses. Mesh topology is very reliable and good for big networks that need to keep running even if some parts fail. Tree topology is good for big networks that often change or grow23.
Choosing the right network topology is crucial for network performance and growth. A well-planned network can speed up data transfer, reduce failures, and make fixing problems easier. Each network type has its own level of complexity and reliability, helping businesses pick the best one for them2324.
FAQ
What is network topology?
Network topology shows how devices and links are set up in a computer network. It tells us how these parts work together.
Why is understanding network topology important?
Knowing about network topologies helps in making networks that work well and are strong.
How many types of network topology are there?
There are many types, like bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree topologies.
What is point-to-point topology?
Point-to-point is when two nodes talk to each other directly. One sends and the other receives. It’s fast and used in things like phone calls and satellite communications.
What is mesh topology?
Mesh topology connects every device to every other through special channels. This makes sending messages fast and reliable. It’s used in important systems like military communications and the internet.
What is star topology?
In star topology, all devices link to a central hub. This hub manages the network. It’s simple to set up and reliable. Often seen in local networks and wireless setups.
What is bus topology?
Bus topology has all devices on one cable, forming a line. It’s cheap and easy to set up but can get slow and unreliable. It suits small networks and cable TV.
What is ring topology?
Ring topology connects devices in a circle, where data moves one way. It’s good at sending data and has a backup plan. Used in big networks and phone systems.
What is tree topology?
Tree topology is a network that looks like a tree. It lets data flow in a clear order. It’s great for big companies with many departments. It grows well and helps find problems easily.
What is hybrid topology?
Hybrid topology mixes different network types. It lets networks be customized for special needs. Hybrid is used in complex networks needing various connections.
Why is network topology important for network administrators?
Network topology is key for building strong and efficient networks. Knowing about different topologies helps admins make smart choices when setting up and running networks.
Source Links
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/network-topology – What Is Network Topology? – Definition from SearchNetworking
- https://www.zenarmor.com/docs/network-basics/what-is-network-topology – Network Topologies. Definition, Types, Examples and Importance – zenarmor.com
- https://www.itglue.com/blog/network-topology/ – What is Network Topology? Types & How to Map It | IT Glue
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/tip/6-types-of-enterprise-networking-topologies – 6 types of network topologies | TechTarget
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/types-of-network-topology/ – Types of Network Topology – GeeksforGeeks
- https://www.spiceworks.com/tech/networking/articles/what-is-network-topology/ – Network Topology Diagrams and Selection Best Practices for 2022
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/point-topology – Point Topology – an overview
- https://www.siklu.com/point-to-multi-point-network-topology/ – Point to Multi-Point Network Topology | Siklu mmWave
- https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/mesh-topology/ – What is Mesh Topology? How Does Data Travel in a Mesh Network
- https://www.zenarmor.com/docs/network-basics/what-is-star-topology – A Guide to Star Topology. Definition, Practices, and Importance – zenarmor.com
- http://www.mindsensors.com/content/86-can-and-its-topology – CAN and its Topology – mindsensors.com
- https://forum.arduino.cc/t/understanding-star-topology-can-bus/1070410 – Understanding star topology (CAN-Bus)
- https://www.ituonline.com/blogs/bus-topology/ – Bus Topology : Understanding The Basics And Benefits – ITU Online
- https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/bus-topology/ – What is a Bus Topology & How Does it Work?
- https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/r/ringtopo.htm – What is a Ring Topology?
- https://www.zenarmor.com/docs/network-basics/what-is-tree-topology – A Guide to Tree Topology. Definition, Practices, and Importance – zenarmor.com
- https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/what-is-tree-topology/ – What is Tree Topology? | Lenovo US
- https://www.cdebyte.com/news/566 – 4 Common CAN Bus Topology Types
- https://www.zenarmor.com/docs/network-basics/what-is-hybrid-topology – A Guide to Hybrid Topology. Definition, Practices, and Importance – zenarmor.com
- https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/what-is-hybrid-topology/ – What is Hybrid Topology? Explained for the Non-Tech Savvy
- https://www.tatacommunications.com/knowledge-base/what-is-hybrid-topology-in-networking-definition-advantages-examples/ – Hybrid Topology In Networking | Definition | Advantages & Examples
- https://www.extnoc.com/learn/networking/network-topology – What is Network Topology?
- https://www.ninjaone.com/it-hub/endpoint-management/what-is-network-topology/ – What Is Network Topology? | Definition | NinjaOne
- https://www.autopi.io/blog/can-bus-explained/ – CAN Bus for Beginners: Everything You Need to Know